Password Spraying Attacks: Detecting and Preventing Credential-Based Threats
In today’s interconnected world, where cybersecurity is of paramount importance, password security plays a crucial role in protecting sensitive information. However, cybercriminals are constantly devising new tactics to breach security measures and gain unauthorized access to user accounts. One such method that poses a significant threat is password spraying attacks. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of password spraying attacks, understand their techniques, and explore effective strategies to detect and prevent these credential-based threats. Let’s dive in and fortify our defenses against these malicious activities.
https://us.norton.com/blog/emerging-threats/password-spraying
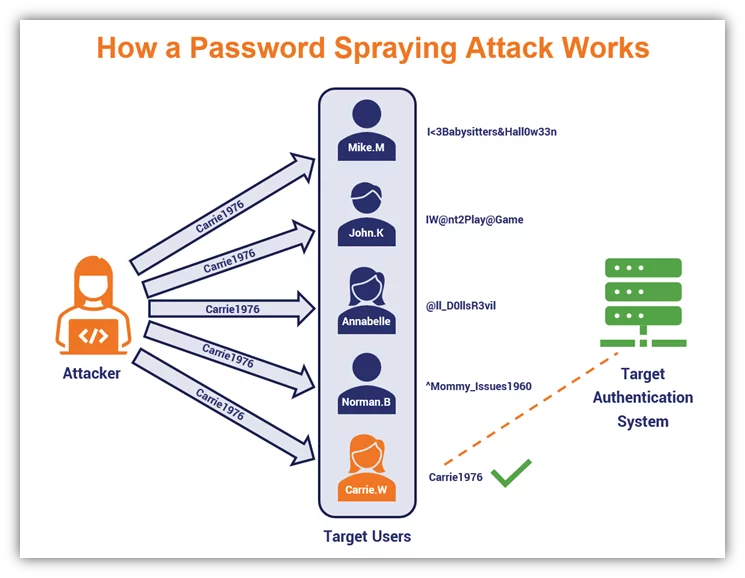
What is a Password Spraying Attack ?
Password spraying attacks are a stealthy approach employed by cybercriminals to gain unauthorized access to user accounts. Unlike brute force attacks, where a single password is repeatedly attempted on different accounts, password spraying involves using a single commonly-used password against multiple usernames. This approach aims to bypass traditional security measures that detect and block repeated login attempts. By targeting multiple accounts simultaneously, attackers increase their chances of finding weak passwords and gaining access.
Steps in Password Spraying Attacks
The attack typically involves the following steps:
Obtaining a list of valid usernames:
The attackers often gather usernames from various sources, such as social media, public employee directories, or other public sources.
Selecting common passwords:
Attackers choose a few commonly used passwords or those known to be weak, such as “password,” “123456,” or “qwerty.”
Spraying passwords across multiple accounts:
The attackers attempt to log in to numerous accounts using the selected passwords for each username.
Evading detection:
Since the attack distributes login attempts across different accounts and uses a limited number of passwords, it can be harder for security systems to detect the attack.
The Significance of Credential-Based Threats
Credential-based threats pose a substantial risk to individuals and organizations alike. When attackers successfully compromise user credentials, they gain access to sensitive information, financial resources, and confidential data. The consequences of such breaches can be severe, including financial loss, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties. Here are some alarming statistics highlighting the gravity of the issue:
• According to a report by Verizon, compromised credentials were responsible for 61% of data breaches in 2020.
• A survey conducted by Google revealed that approximately 25% of users reuse the same password across multiple accounts, increasing the potential impact of password spraying attacks.
• The average time it takes for an organization to identify a credential-based breach is around 280 days, as per a study by the Ponemon Institute.
• Password Issues: A whopping 80% of hacking breaches are linked to password vulnerabilities.
• Reusing Passwords: Alarmingly, 54% of employees reuse passwords for both work and personal accounts.
• Managing Passwords: On average, people juggle around 100 passwords to secure their digital lives.
• Same Password for All: Surprisingly, 13% of Americans use a single password across all their accounts.
• Commonly Weak: Shockingly, a staggering 23 million accounts still cling to the infamous password “123456.”
https://www.thesslstore.com/blog/brute-force-attack-definition-how-brute-force-works/
The Role of Brute Force Attacks and Password Guessing
While password spraying attacks differ from brute force attacks and password guessing techniques, understanding these related threats is crucial for a comprehensive defense strategy.
Brute Force Attacks:
Brute force attacks adopt a systematic approach, tirelessly attempting every possible password combination until the correct one is successfully uncovered. Implementing account lockouts, CAPTCHA challenges, and rate limiting can help mitigate the risk of brute force attacks.
Password Guessing:
Attackers often exploit weak or easily guessable passwords. Educate users about password best practices, including avoiding common passwords, personal information, and predictable patterns.
Detecting Password Spraying Attacks
Early detection of password spraying attacks is crucial to preventing unauthorized access to user accounts. Implementing robust detection mechanisms can help organizations stay one step ahead of cybercriminals.
Here are some effective methods for detecting password spraying attacks:
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS):
IDS tools monitor network traffic and flag suspicious login activities. They analyze login attempts, account lockouts, and authentication failures to identify potential password spraying attacks.
Security Monitoring:
Continuous monitoring of user login activities and abnormal patterns can help identify potential breaches. Monitoring tools can track login attempts from unusual locations, multiple failed login attempts, or a sudden surge in account lockouts.
Threat Intelligence:
Utilizing threat intelligence services enables organizations to stay informed about emerging password spraying techniques and attack trends. This information can help identify and respond to potential threats more effectively.
Anomaly Detection:
Implementing anomaly detection systems can identify unusual login behavior, such as a sudden increase in failed login attempts or login activity from atypical locations. Machine learning algorithms can analyze patterns and identify potential password spraying attacks.
User Behavior Analysis:
Analyzing user behavior can help detect suspicious activities. Deviations from normal behavior, such as login attempts outside of regular working hours or simultaneous login attempts from different geographic locations, can be red flags for password spraying attacks.
Preventing Password Spraying Attacks
Prevention is always better than mitigation when it comes to cybersecurity. By implementing proactive measures, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to password spraying attacks.
Consider the following prevention strategies:
Strong Password Security:
Enforce password complexity requirements, such as a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Encourage users to create unique passwords for each account and avoid easily guessable information.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
Implement MFA, which adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide additional verification, such as a unique code sent to their mobile device, in addition to their password.
Regular Risk Assessments:
Conduct comprehensive risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities in your organization’s authentication system. This includes evaluating password policies, user account management procedures, and access controls.
Security Awareness Training:
Educate users about password security best practices, emphasizing the importance of creating strong passwords, avoiding password reuse, and detecting phishing attempts.
Access Controls:
Implement strict access controls, limiting user privileges to only what is necessary for their roles. Regularly review and update user permissions to ensure that access remains appropriate and up to date.
Real-World Examples
Examining real-life incidents involving password spraying attacks can provide valuable insights into the impact of these threats. Here are a few notable examples:
1. DailyQuiz – DailyQuiz (previously known as ThisCrush) faced a severe breach, opening the door for hackers to infiltrate a massive database containing nearly 13 million user accounts. The attackers successfully pilfered plaintext passwords, email addresses, and IP addresses belonging to 8.3 million users. Shockingly, they opted to sell this stolen data on the elusive Dark Web. By May, the compromised information had spread far and wide through various data brokers, ultimately becoming accessible to the general public.
Many organizations commit a critical error by storing sensitive user details in plaintext. Recognizing that no database is entirely invulnerable, encrypting the stored data becomes paramount. In the unfortunate event of a hacker breaching your database, encryption renders the information indecipherable, rendering it useless to them.
2. Vekarda – Verkada, a prominent security company, recently faced a devastating cyberattack, leading to unauthorized access to sensitive customer data. The hackers compromised more than 5,000 security cameras, providing them with an unsettling view inside hospitals, jails, schools, Equinox gyms, Tesla factories, and warehouses. The impact extended further, with eight customers experiencing Access Control product data breaches, exposing badge credentials. Additionally, another eight customers had their WiFi credentials compromised, raising serious concerns about privacy and security.
In a daring cyber intrusion, the hacking collective targeted Verkada’s systems through an admin password exposed on a misconfigured customer support server. Gaining entry, they accessed customer cameras and Verkada’s sales orders, but despite their efforts, the hackers could not penetrate Verkada’s internal systems. A testament to the company’s robust security measures!
Swift and decisive, Verkada responded to the breach by severing hackers’ access just two hours after detection. Within an impressive six-hour window, they promptly informed their customers about the incident.
Building a Comprehensive Password Security Strategy
A robust password security strategy is essential to protect against password spraying attacks and other credential-based threats. Consider the following best practices:
Assess Current Password Practices
Evaluate your current password practices across all systems and accounts. Identify any weak points, such as reused or easily guessable passwords, and take note of areas that require improvement.
Implement Strong Password Policies
Enforce strong password policies for all users. Require passwords to be of sufficient length, containing a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Discourage common words or easily guessable patterns.
Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Introduce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) wherever possible. Require users to provide an additional form of identification, such as a one-time code sent to their mobile device, along with their password for enhanced security.
Utilize Password Managers
Encourage the use of password managers to store and manage complex passwords securely. These tools help users generate strong passwords and eliminate the need to remember multiple login credentials.
Regularly Update Passwords
Institute a policy of regular password updates. Prompt users to change their passwords at defined intervals, reducing the risk of prolonged exposure to potential threats.
Educate Users on Phishing Awareness
Train users to recognize and avoid phishing attempts, as attackers often use deceptive tactics to steal passwords. Educate them on the importance of verifying links and never sharing login credentials via email or unknown websites.
Conduct Security Awareness Training
Conduct regular security awareness training sessions to keep employees informed about evolving password security best practices and potential threats.
Apply Account Lockouts and Rate Limiting
Configure account lockout policies and rate limiting mechanisms to automatically block login attempts after a certain number of failed tries, making brute force attacks less effective.
Regular Security Audits
Conduct periodic security audits to assess the effectiveness of your password security strategy. Identify any gaps or weaknesses and make necessary adjustments to stay ahead of potential threats.
Optimize your password security settings:
No matter the platform, prioritize a thorough review and configuration of password security settings. For instance, on Microsoft Azure’s cloud-only environment, leverage the free Azure AD Password Protection. It identifies and bars known weak passwords, and can even block organization-specific terms. For on-premises and hybrid setups, a license is needed, but the robust security it offers is worth the investment.
Password Rotation Policies:
Establish policies that require regular password changes to minimize the risk of compromised credentials.
Monitoring and Incident Response:
Implement robust monitoring systems to detect password spraying attacks and develop an incident response plan to handle potential breaches effectively.
By following these steps, you can build a robust and comprehensive password security strategy that significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Dealing with a Password Spraying Attack: Post-Incident Measures to Implement
Reset Privileged Passwords:
Without MFA, immediately reset passwords for privileged and admin domain accounts.
Enhance Logging:
Configure your security logging platform to monitor failed login attempts across various systems and trigger prompt responses and investigations.
Utilize EDR Technology:
Deploy Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) or Deception Technology to identify malicious activities and block lateral movement by hackers.
Review Incident Response Plans:
Review and activate incident response plans, alerting appropriate team members as a precautionary measure.
Seek Expert Support:
Engage a security firm with digital forensic and incident response capabilities to identify compromised accounts, investigate potential data loss, and provide additional support.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the threat of password spraying attacks remains a constant concern for individuals and organizations in today’s digital landscape. However, armed with knowledge and proactive defense strategies, we can mitigate the risks and protect our valuable information. By prioritizing strong passwords, implementing multi-factor authentication, maintaining continuous monitoring, and educating users about password security, we can establish a robust password security strategy. Let us remain vigilant, stay secure, and keep our valuable information out of the reach of cybercriminals.
Resources :
https://fieldeffect.com/blog/password-spraying-attacks-detection-revention/
https://www.loginradius.com/blog/identity/password-spraying/
https://www.varonis.com/blog/password-sprayinghttps://blog.netwrix.com/2020/10/28/password-spraying/
https://www.splunk.com/en_us/blog/learn/password-spraying.html
https://www.splunk.com/en_us/blog/security/detecting-password-spraying-attacks-threat-research-release-may-2021.html
https://auth0.com/blog/what-is-password-spraying-how-to-stop-password-spraying-attacks/
https://www.crowdstrike.com/cybersecurity-101/password-spraying/
https://www.onelogin.com/learn/6-types-password-attacks
https://www.lepide.com/blog/what-is-password-spraying-and-how-to-stop-it/
https://spanning.com/blog/password-spraying/
https://owasp.org/www-community/attacks/Password_Spraying_Attack
https://www.keepersecurity.com/threats/password-spraying-attack.html
https://www.verizon.com/about/news/verizon-2021-data-breach-investigations-report
https://rshostinginfo.com/Website-Security/details/226/Common-Website-Security-Threats-and-How-to-Protect-Against-Them
https://www.enzoic.com/blog/8-stats-on-password-reuse/
https://www.ponemon.org/library/2019-credential-stuffing-report/




