Widening Base of Internet Consumption in India and the Need for Cyber Literacy

In the four decades since its foundation, the Internet has gone through a lot of dramatic changes and enabled flows of information, including news, entertainment, financial and academic data. In addition, it has brought the world closer via interpersonal communication like email, instant messaging, video calling, and social networking, along with allowing the consumers to purchase anything anytime virtually and providing the producers with direct access to a wide range of markets.
Also, the Internet is bustling with spurred entrepreneurship and is supported by a variety of industries and large organizations. In addition, the government has benefited from online productivity tools and communication advancements as well as helped to broaden their services to citizens and improve delivery. In a short span, it has become impossible for most of us to imagine a world without the internet.
Internet Usage in India
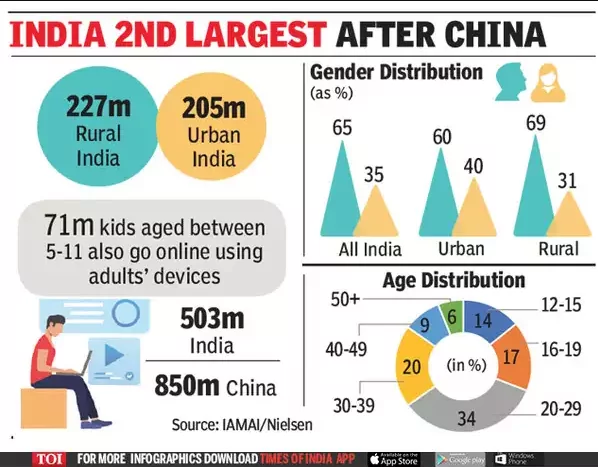
According to the IAMAI-Kantar ICUBE 2020 report, with over 622 million internet users and the Indian internet market blooming rapidly, India is the second largest online market in the world after China. It had increased by over 150% since 2019 when the count of internet users was around 300 million, and it is estimated that by 2023 there will be over 650 million internet users in the country. Moreover, the internet penetration rate of India stands at 52% currently, which makes it one of the most important countries for international organizations that deal with online marketing and e-commerce.
Source: TOI
The internet users in India access the internet for entertainment, communication, and regularly shopping online, along with activities like learning, video streaming, and gaming. These users use social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, or Instagram to connect with friends and family members or for entertainment purposes as well as to present their opinions regarding the latest news events. They also use YouTube or other video-based platforms to share their thoughts on personal experiences, create vlogs, videos, and many more. Most of today’s generation has grown up using computers and technology from an early age and can relate to modern technologies better than older generations. According to IAMAI-Kantar ICUBE 2020 report, several aspects of these users are based on:
- Age Group – Almost 7 million children between the age of 5-11 use the internet in India. 40% belong to the early age of 15-34, and another 20% are between the age of 20-24 years.
- Region – More than 50% of active internet users are from rural areas, while the urban region seems to have hit a plateau. Small towns report almost two out of every five active internet users in the country.
- Gender – The ratio of male to female active internet users is 65% are men, and 35% are female, which is almost the same for both urban and rural India.
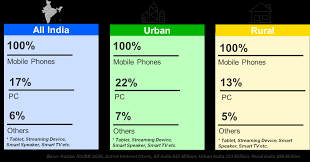
Moreover, the device of choice for accessing the internet in both urban and rural areas are mobile devices as they are relatively cheap and have low tariff plans, while the remaining 17% use personal computers and 6% access it through tablets, streaming devices, smart speakers, and smart televisions.
Source: Kantar ICUBE
In the past few years, the use of the internet in India has increased significantly, more people in rural and urban areas are gaining access to the internet as mobile phones, and internet services have become affordable for the people. This increasing use of internet consumption gives rise to the need for cyber literacy in India.
Need for Cyber Literacy
Today, in a society where communication and access to information are increasing through digital technologies like internet platforms, social media, and mobile devices, it is particularly important for the people of India to understand the internet and the devices that they access it. They should know how to protect their data from cyberattacks, phishing, finding information in faster and safer ways, and much more.

Source: Iris
According to a recent survey, it has been found that even though people have heard about data breaches, most of them have failed to change their security habits, only one-quarter of employees use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), and just one-third have decreased their use of open Wi-Fi hotspots. In addition, it has been found that 45% of people make use of a Personal Identification Number (PIN) to lock their devices, while 19% use some form of biometric tool. This shows the ignorance, misunderstanding, and denial of people towards data protection and cybersecurity. This can lead to severe consequences like cyberattacks, data thefts, identity thefts, etc. To avoid such scenarios, it is important to understand cyber terminology, threats, and opportunities and find accurate and reliable resources in cyber intelligence.
Examples of cyber literacy include:
- Being able to determine the legitimacy of a website
- Safe searching/downloading practices to avoid viruses and phishing scams
- Understanding which information is suitable to be safely posted on social networking sites
- Being conscious of the actions being done and taking place online and motivations.
Conclusion
In today’s age, in the past few years, there has been a drastic increase and change in the consumption of the internet in India, ranging from rural and urban areas and age groups to the mode of access. With this increasing use of the internet, the necessity for cyber literacy has also increased, and people should know how to protect themselves from cyberattacks and cybercrimes.
References
- United States Cybersecurity Web Magazine
- McKinsey
Author,
Devyani Shete,
Managed SOC Dept.
Varutra Consulting Pvt. Ltd.