Understanding Sniffing Attacks: How They Work and How to Stay Protected
Introduction
In today’s interconnected world, where information is transmitted over networks on a daily basis, it is crucial to understand the threats posed by malicious actors. One such threat is the sniffing attack, a technique employed by cybercriminals to intercept and capture network traffic. In this blog post, we will explore into the inner workings of sniffing attacks, uncover their potential risks, and provide valuable insights on how to protect yourself and your sensitive data.
1. What are Sniffing Attacks?
Sniffing attacks involve intercepting and analyzing network traffic to capture sensitive information, making them a significant type of network-based attack. By exploiting network vulnerabilities, attackers gain unauthorized access to network packets, allowing them to eavesdrop on conversations, gather usernames and passwords, and even extract valuable data.
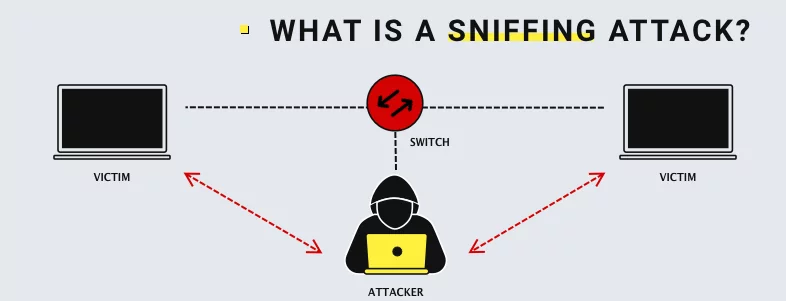
https://gridinsoft.com/blogs/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/what-is-a-sniffing-attack.png
According to a study by the Ponemon Institute, 67% of organizations have experienced a data breach in the past two years. Of those breaches, 23% were caused by sniffing attacks.
In 2022, the global cost of data breaches is expected to reach $6 trillion. Of that cost, $1 trillion is expected to be due to packet sniffing attacks.
It is essential to understand the different types of sniffing attacks, including ARP spoofing, DNS spoofing, and packet sniffing, to effectively combat this threat.
2. How do Sniffing Attacks Work?
Sniffing attacks follow a step-by-step process, starting with attackers gaining access to the target network. Once inside, they use specialized tools to intercept and capture network packets. These tools allow them to analyze the captured data and extract sensitive information.
To illustrate this, let’s take an example of an attacker targeting a public Wi-Fi network. By setting up a rogue access point and conducting an ARP spoofing attack, the attacker can redirect network traffic through their device, giving them complete visibility into the transmitted data. This could potentially expose usernames, passwords, credit card details, and other confidential information.
Types of Sniffing Attacks
Packet sniffing attacks can be categorized into two types: active and passive.
Active Packet Sniffing
Active packet sniffing attacks involve the injection of a new protocol into the network or a user’s computer. This allows the hacker to reroute legitimate packets and traffic to their storage device. Examples of active packet sniffing attacks include spoofing attacks, DHCP attacks, and DNS poisoning.
DNS Spoofing
DNS (Domain Name System) Spoofing ( DNS cache poisoning), is when an attacker redirects traffic meant for a legitimate domain to a malicious website. It works by manipulating the DNS cache of a target network’s Domain Name Server. DNS Spoofing allows the attacker to steal sensitive data entered by victims on the fake website, leading to identity theft or other fraudulent activities.
DHCP Spoofing
DHCP spoofing is a vital security feature designed to protect networks connected to the Internet. It acts as a robust security mechanism that safeguards against malicious attacks by preventing unauthorized interception or alteration of messages exchanged between network clients and DHCP servers. By implementing DHCP spoofing, organizations can fortify their network infrastructure and ensure the integrity and confidentiality of their communications.
Passive Packet Sniffing
On the other hand, passive packet sniffing attacks take a more indirect approach. Hackers monitor the network or hub, intercepting and examining packets as they pass by. In this scenario, the attackers simply observe the same packets that your security team sees, effectively stealing administrative access to the hub. Since there is no direct injection or traceable attack, passive packet sniffing attacks are harder to detect.
a. Network Eavesdropping
Passive sniffing attacks often involve network eavesdropping, where an attacker silently monitors network traffic without actively interfering. By capturing and analyzing data packets as they pass through the network, the attacker can gather sensitive information, such as login credentials, email contents, or financial transactions, without the knowledge of the targeted users.
b. Wireless Packet Sniffing
Wireless networks are susceptible to passive sniffing attacks, where attackers intercept and analyze wireless network traffic. By leveraging tools like Wireshark, attackers can capture and examine data packets transmitted over the airwaves. This allows them to extract valuable information, such as passwords or sensitive business data, compromising the security of the wireless network and the devices connected to it.
Classification of sniffing attacks based on various scenarios.
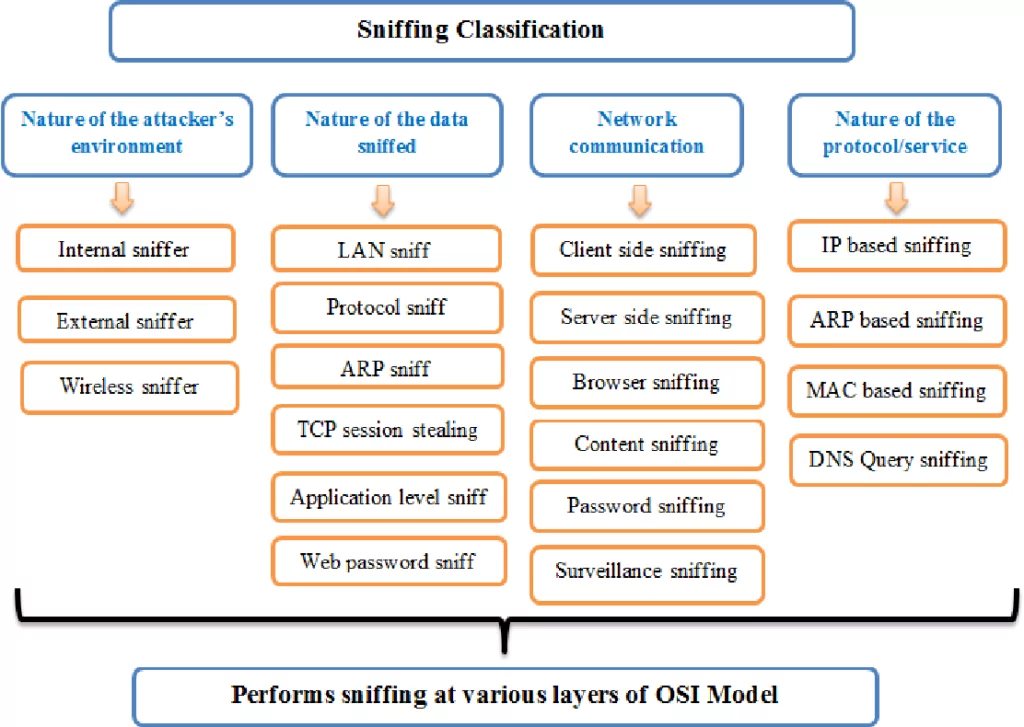
Semanticshoclar.org
3. Common Targets of Sniffing Attacks
Sniffing attacks can target various entities, including personal devices, public Wi-Fi networks, and corporate networks. Personal devices connected to unsecured networks are particularly vulnerable. Research shows that a staggering number of individuals connect to public Wi-Fi networks without considering the security risks involved. These networks often lack encryption and provide a prime opportunity for attackers to launch sniffing attacks.
Corporate networks, on the other hand, present a valuable target due to the potentially sensitive and proprietary information they hold. Successful sniffing attacks on these networks can result in severe consequences, such as financial loss, reputational damage, and legal repercussions.
4. Risks and Consequences
The risks and consequences of falling victim to a sniffing attack are significant. Data breaches resulting from sniffing attacks have become increasingly prevalent, affecting both individuals and organizations. The exposed information can be misused for identity theft, financial fraud, or corporate espionage.
Notably, the consequences extend beyond the immediate financial impact. Companies that fail to protect their customers’ data may suffer from a loss of trust, leading to a decline in business and tarnished reputation.
5. Protecting Against Sniffing Attacks
Staying protected against sniffing attacks requires implementing robust security measures. Here are essential points to consider:
Encryption: Encryption is a powerful defense against sniffing attacks. It ensures that data transmitted over networks remains secure and unintelligible to potential attackers. Employing protocols like HTTPS, SSL/TLS, and VPNs is crucial to encrypt sensitive information.
Network Segmentation: Segregating networks into smaller subnetworks limits the scope of a potential sniffing attack. By isolating sensitive data and limiting access, even if an attacker gains access to one network segment, they will have restricted visibility.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): IDS/IPS solutions can identify and block suspicious network traffic, raising alerts and taking preventive actions against potential sniffing attacks.
Regular Software and Firmware Updates: Keeping all software and firmware up to date is crucial in preventing sniffing attacks. Developers often release updates to patch vulnerabilities and improve security measures. By promptly applying these updates, you close off potential entry points for attackers.
Strong Passwords and Authentication: Implementing strong, unique passwords for all accounts and systems is a fundamental security practice. Additionally, consider using multi-factor authentication (MFA) whenever possible.MFA adds an extra layer of protection, making it significantly harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
Secure Wi-Fi Networks: When connecting to Wi-Fi networks, especially in public spaces, exercise caution. Avoid connecting to unsecured networks and prioritize networks that use encryption protocols, such as WPA2 or WPA3. If necessary, use a trusted virtual private network (VPN) to encrypt your internet traffic, ensuring the confidentiality of your data.
User Education and Awareness: The human element is often the weakest link in the security chain. Educating yourself and your employees about the risks of sniffing attacks and the best security practices is crucial. Regular security awareness training can help individuals identify potential threats, avoid risky online behavior, and understand the importance of staying vigilant.
Network Monitoring and Logging: Implementing comprehensive network monitoring and logging systems can help detect abnormal network activity. By closely monitoring network traffic, you can identify potential signs of sniffing attacks, such as sudden spikes in traffic or unusual patterns. Logging network activities can provide valuable evidence in the event of a security incident.
Penetration Testing: Conducting regular penetration tests can help identify vulnerabilities in your network infrastructure. By simulating real-world attack scenarios, you can uncover weaknesses and take appropriate measures to strengthen your defenses against sniffing attacks.
Data Encryption at Rest and in Transit: In addition to encrypting data during transmission, it is vital to consider data encryption at rest. Encrypting stored data, whether on servers, databases, or individual devices, adds an extra layer of protection. This way, even if attackers manage to access the data, it remains unreadable and unusable.
6. Network Security Measures
Network security measures play a pivotal role in preventing and mitigating the risks associated with sniffing attacks. Let’s take a closer look at some essential measures:
Firewalls: Firewalls act as a barrier between an internal network and external networks, controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined security rules. They play a crucial role in detecting and blocking unauthorized access attempts, including those from sniffing attackers.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS): IDS and IPS solutions monitor network traffic for suspicious activities and potential security breaches. IDS identifies and raises alerts for suspicious behavior, while IPS takes immediate action to prevent the identified threats. These systems are instrumental in detecting and stopping sniffing attacks before they cause significant harm.
Regular Software and Firmware Updates: Keeping all software and firmware up to date is vital in preventing sniffing attacks. Developers continually release updates to patch vulnerabilities and enhance security measures. By promptly applying these updates, you close off potential entry points for attackers, reducing the risk of successful sniffing attacks.
7. Securing Wi-Fi Networks
Public Wi-Fi networks pose inherent vulnerabilities, making them prime targets for sniffing attacks. It is essential to understand the risks associated with public Wi-Fi and take appropriate measures to secure your network connections
Vulnerabilities of Public Wi-Fi Networks: Public Wi-Fi networks often lack encryption, allowing attackers to intercept and capture unencrypted data transmitted over the network. This can include personal information, login credentials, and financial details. Sniffing attacks on public Wi-Fi networks are particularly concerning due to their prevalence in public spaces such as cafes, airports, and hotels.
Guidelines for Securing Wi-Fi Networks: To enhance the security of your Wi-Fi network, consider the following steps:
i. Change the default administrator credentials for your Wi-Fi router to prevent unauthorized access.
ii. Enable Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2) or the more recent WPA3 encryption protocols to secure your network.
iii. Disable remote administration of your Wi-Fi router to prevent external manipulation.
iv. To ensure both optimal performance and robust security, it is crucial to periodically update the firmware of your Wi-Fi router.
Benefits of Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): Utilizing a VPN can provide an additional layer of security when connecting to Wi-Fi networks, particularly in public settings. VPNs encrypt your internet traffic, making it significantly harder for sniffing attackers to intercept and decipher your data. By routing your traffic through a secure VPN server, you establish a secure and private connection, regardless of the Wi-Fi network you are connected to.
8. Identifying Signs of Sniffing Attacks
Recognizing potential signs of a sniffing attack is crucial in mitigating the risks. Keep an eye out for the following indicators:
a. Slow Network Performance: If your network experiences significant and unexplained slowdowns, it could indicate the presence of a sniffing attack. The interception and analysis of network traffic by attackers can consume network resources, leading to reduced performance.
b. Unexpected Network Activity: Monitor your network for any unusual or unauthorized network activity. Suspicious connections or devices accessing your network without your knowledge may indicate a sniffing attack.
c. Suspicious Log Entries: Reviewing system and network logs can provide valuable insights into potential sniffing attacks.
Monitor the following indicators for suspicious and unusual log entries:
i. Unusual Source and Destination IP Addresses: Look for IP addresses that are not typically associated with your network or communication patterns. These could indicate attempts to intercept network traffic.
ii. Failed Authentication Attempts: Multiple failed login attempts from different sources can be a sign of an attacker trying to gain unauthorized access and potentially launch a sniffing attack.
iii. Unusual Network Protocols or Port Scans: Monitor for unusual network protocols or unexpected port scans. These activities can indicate reconnaissance attempts by attackers preparing for a sniffing attack.
iv. Anomalies in Network Traffic Patterns: Look for significant deviations from normal network traffic patterns. Sudden spikes or unusual patterns can be indicative of a sniffing attack in progress.
9. Educating Users and Employees
One of the most effective ways to prevent sniffing attacks is through user education and awareness. Implement the following measures to enhance user knowledge and protect against such attacks:
a. Importance of User Education: Educate users about the risks associated with sniffing attacks, emphasizing the importance of staying vigilant and adopting best security practices.
b. Strong Passwords and Good Browsing Habits: Encourage users to create strong, unique passwords and avoid using the same password across multiple accounts. Additionally, educate them about the dangers of clicking on suspicious links or downloading files from untrusted sources.
c. Regular Security Awareness Training: Provide regular security awareness training for employees, focusing on the risks of sniffing attacks and how to identify and report potential threats. Cover topics such as phishing, social engineering, and safe internet browsing habits.
10. Notable Sniffing Attack Incidents in the Recent Times
Examining real-life examples of sniffing attacks can provide valuable insights into the consequences and lessons learned from such incidents:
a. The Colonial Pipeline Attack: In 2021, the Colonial Pipeline, a major fuel pipeline in the United States, was hit by a ransomware attack. The attack caused the pipeline to shut down for several days, which led to gasoline shortages and price hikes across the country. The attack was carried out by a group of hackers called DarkSide. The hackers were able to gain access to the pipeline’s computer systems by exploiting a vulnerability in a software application that was used by the pipeline. Once they had access to the systems, the hackers were able to encrypt the data and demand a ransom payment in exchange for the decryption key. The pipeline company paid the ransom, but the hackers later released the decryption key anyway.
Lesson learned: This attack highlights the importance of having strong security measures in place for critical infrastructure systems. In particular, businesses should make sure that their systems are up to date with the latest security patches and that they have strong passwords and security policies in place.
b. The JBS Meatpacking Plant Attack: In 2021, JBS, a major meatpacking company in the United States, was hit by a ransomware attack. The attack caused the company to shut down several of its plants, which led to meat shortages and price hikes across the country. The attack was carried out by a group of hackers called REvil. The hackers were able to gain access to the company’s computer systems by exploiting a vulnerability in a software application that was used by the company. Once they had access to the systems, the hackers were able to encrypt the data and demand a ransom payment in exchange for the decryption key. JBS paid the ransom, but the hackers later released the decryption key anyway.
Lesson learned: This attack highlights the importance of having strong security measures in place for critical infrastructure systems. In particular, businesses should make sure that their systems are up to date with the latest security patches and that they have strong passwords and security policies in place.
Conclusion
Understanding sniffing attacks and implementing the necessary protective measures is vital in safeguarding sensitive information and preventing data breaches. By utilizing network security measures, securing Wi-Fi networks, identifying signs of sniffing attacks, educating users, and learning from real-life examples, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to these attacks.
Remember, staying informed, adopting best security practices, and maintaining a proactive approach to cybersecurity are essential in our increasingly connected world. Stay vigilant, protect your networks, and prioritize the security of your valuable data.
Research, References & Resources :
https://www.eccouncil.org/cybersecurity-exchange/ethical-hacking/what-are-sniffing-attacks/
https://www.comparitech.com/blog/information-security/sniffing-attack/
https://securiumsolutions.org/sniffing-attacks-types-tools-and-how-to-prevent/
https://www.iansresearch.com/resources/all-blogs/post/security-blog/2022/08/11/how-to-prevent-and-detect-packet-sniffing-attacks
https://intellipaat.com/blog/tutorial/ethical-hacking-cyber-security-tutorial/sniffing-attacks/
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/what-is-sniffing-attack-in-system-hacking/
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/ethical_hacking/ethical_hacking_sniffing.htm
https://cisomag.com/what-are-sniffing-attacks-and-how-to-defend-against-them/
https://www.techslang.com/definition/what-is-a-sniffing-attack/
https://www.greycampus.com/opencampus/ethical-hacking/sniffing-and-its-types/
https://www.spiceworks.com/it-security/network-security/articles/what-is-packet-sniffing/
https://www.knowledgehut.com/blog/security/packet-sniffing
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/ethics-packet-sniffing-legal-ethical-sniff-network-traffic




