Zero Trust Maturity Model
What is Zero Trust?
Zero Trust is a Cybersecurity terminology that requires all users even those who are inside the organizational corporate network to be authenticated thus validating security structure before being allowed access to resources, information, and data.
The maturity model feeds advanced technologies such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), identity and access management (IAM) as well as advanced security technologies to verify the user’s identity and sustain system management security.
Zero Trust maturity model advice that organizations should not directly trust anything inside or outside of network perimeter and should validate everything that tries to connect to systems and applications before allowing access.
The first Zero Trust model of cybersecurity was developed in 2010 by Forrester but it was not completed due to limitations in multiple areas. 6 years later in 2016,Google successfully developed as well as implemented their version of Zero Trust model.
The Zero Trust always follows the principle “never trust, always verify”. The legacy approach automatically trusted users and endpoints within the organization’s perimeter, putting the network at risk from malicious actors and allowing unauthorized users.
Zero Trust is capable to validate that a user and devices have the right privilege on the basis of policy configuration. In today’s secure technology savvy environment one-time validation is not sufficient due to advanced threats and attacks pattern evolved globally.
Organizations must ensure that all access requests are continuously validated in order to allow connections to any of network devices or assets both on premise as well as on cloud.
Today’s organizations require a new secure technology that adequately adapts to the complexity of the current environment, protect its users, applications, and sensitive data wherever they are placed.
Importance of Zero Trust:
Many organizations are considering that everything behind the security device like firewall is safe and enough but depending upon a single security solution is not an effective strategy to secure organizational assets.
Zero Trust is one of the effective ways for organizations to control access to their networks, applications, and data. It provides a preventive approach including verification and validation to prevent unauthorized access.
In this model, every request of access is highly authenticated and authorized as per the policy created and inspected for any suspicious activity before providing access.
Post network segmentation and restricting user’s access, Zero Trust security model helps the organization to prevent breaches and reduce potential damages from threat actors. This approach helps to identify what happened and what was compromised as well as how to prevent it from happening again on the basis of logs.
The deployment of Zero Trust policies strongly relies on real-time visibility into user’s activity and attributes such as:
- User Identity
- User Logins
- Security or Incident Detection
- Vulnerabilities pertaining to Exploitation, Patching and Scanning
- Patch Levels
- Firmware Versions
- Operating System Versions
The Zero-trust model primarily checks for 3 parameters as listed below:
- Zero Trust for the Workforce:
Users such as employees, partners and vendors accessing work related applications using their personal or enterprise managed systems. This parameter ensures only the legitimate users and authorized solutions / appliances only access applications on the basis of policy configurations.
- Zero Trust for Workloads:
This parameter mainly observes the secure access when API or services accessing a database within an application and whether applications running on any virtualized environment or cloud computing interconnect with each other.
- Zero Trust for the Workplace:
This parameter focuses on secure access for all appliances that integrate the organizations network, such as servers, endpoints, and other security devices etc.
Principles of the Zero Trust Security Model:
Zero Trust model has been developed on concept of directly not trusting any users, devices, networks and access to the important tools based on any single identity types and their related attributes.
Organizations need to provide secure access to their resources to avoid any breaches and to secure organizations assets. Before providing access, they need to verify user’s location, their role in organization, the types of services for data that they are requesting to access. In order to do this efficiently, they need to use automated policy(which includes Machine learning as per the case)of Zero-Trust framework which is integrated with Threat intelligence to maintain security balance.
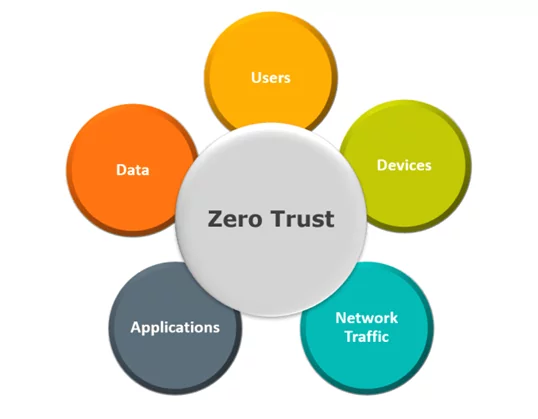
Image Source: https://logrhythm.com
- Users:
User authentication typically has two components that is an identity and password. This provides a layer of defence that helps ensure that when a user is accessing network, they are the authenticated users.
- Devices:
Once the identity has been granted access to the resources, data can flow from variety of different devices depending on the organization’s network infrastructure. Hence, it is recommended to monitor device heath and compliance for secure access.
- Network Traffic:
Network traffic is the amount of data moving across a network and the amount of organizational data that is accessed over network infrastructure. Network controls can provide visibility to prevent attackers from moving laterally across the network.
- Applications:
Applications provide the interface by which data is consumed. These applications may be genuine on network infrastructure, but controls and security technology should be applied to monitor for any abnormal behaviour.
- Information and Data:
Cyber security teams are focused in protecting data, but traditional methodology will not help to protect data against today’s advanced threat actors. Data should be classified, encrypted and access restricted based on the attributes.
Outcome of Zero Trust Model for Cybersecurity:
- The main outcome of this model is that trusted identities get access to the applications, systems, networks, and access to data that is based on their role.
- Another outcome is Data breach prevention from hacking, it cannot stop all breaches, but it gives a chance at containing an incident before it become a breach. The incident involving a compromise of users, devices, network traffic or data and if user is compromised, attacker would still need to compromise the system and network separately to access the valuable information that they are looking.
- If a system is compromised, the attacker still looks to break the other types of identities to gain access on other applications of organization. Here additional authentication methods will help to protect sensitive data.
Zero Trust Model in Organizational Network:
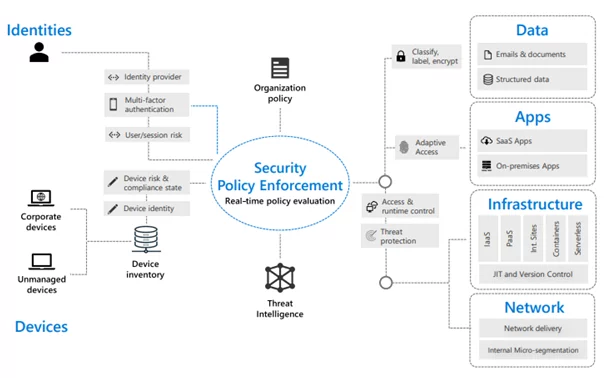
Image Source:www.microsoft.com
In implementation, devices are connected and able to provide the signal which is a function to provide information about the data access. This signal is required to make informed access decisions using automated policy deployment.
As Zero Trust relies on signal and solution integration, to do this effectively, organizations should use automated policy enforcement. The Security Operations Center should have a multi-tier incident response team that uses advanced threat detection to prioritized security alerts. To response any incidents, such as disallowing access to affected devices should be automated to improve response times and minimize the risk.
Below are some requirements that are required to fulfill before implementation of the Zero Trust model:
- To know about sensitive data locations.
- Identify the roles of users within organization and group employees.
- Integrate the transaction flows of all roles to sensitive data storage and to the important data stores, systems and applications needs to do their day-to-day operations.
- Plan and design the Zero Trust network using segregation and segmentation of the network.
- Configure rules on segmentation gateway as per expected behavior of the data which generated by common or trusted sources.
- Monitor the network, analyse the network log traffic, and configure policy based on the intelligence received from cybersecurity analytics.
The Technology behind Zero Trust Model:
The Zero Trust approach depends on various known technologies and governance processes to achieve its mission of securing the organizations enterprises network. This technology checks user’s geographical locations and several parameters before granting access to a specific part of the network.
It verifies whether it is a known secure endpoint and what is security status of this endpoint. Zero Trust works on technologies such as identity and access management (IAM), two-factor authentication (2FA), encryption and file system permissions.
Many organizations are already using the bits of Zero Trust models e.g. Privileged Identity Management (PIM), Plug-gable Authentication Module as well as Identity and Access management, by leveraging IAM, PIM and PAM technologies, Zero Trust is developing security model that no one has access until they have proven they are trusted users.
Conclusion:
The Zero Trust security model is the next evolution of cybersecurity model which is developed on an identity central model for security that is believed to be completely transforming the current and legacy IT security model.
The model is the ultimate solution to building security for the entire organization. While this model is most effective when integrated across the entire digital assets, some organizations may need to take a phased approach that targets specific area for change based on their available resources.
It may not be a complete silver bullet, but it gives the best chance to contain security incidents before they become fatal breaches.
Author,
Akshay Wadkar
Managed SOC Team
Varutra Consulting Pvt. Ltd.




