Learning About Web Application Firewall (WAF) Security

Introduction of Web Application Firewall (WAF) Security
A web application firewall (WAF) is a security solution that provides rule sets to help defend any internet application against attack. Unwanted HTTP traffic to and from the web application is monitored, filtered, and blocked by it.
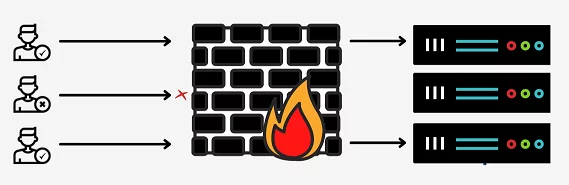 Fig 01 – Process of Web Application Firewall
Fig 01 – Process of Web Application Firewall
It is used to defend against threats and prevent attacks exploiting the vulnerabilities, such as
- SQL injection
- Cross-site scripting (XSS)
- File inclusion
- Improper system configuration.
However, it can also protect against unauthorized access to resources, session hijacking, and other threats. Also, learn about various threats like Mitigating CSRF attacks and Web Cache Deception in our blog section.
How does Web Application Firewall (WAF) Security work?
WAF will examine the GET and POST requests to and. The firewall will discriminate between valid and illegitimate traffic based on the rules that are defined. It can also detect unusual behavioral patterns.
For example, if an attack causes the web application to send back significantly larger responses than intended, then it can identify that aberration and alert.
The crucial point to remember is that it will look at the content of all packets, not just the headers, to block bogus requests, and clever firewalls even challenge requests to force the perpetrator to verify they are human and not a bot.
Types of Security Models in Web Application Firewall (WAF)
A web application firewall is categorized according to three basic security models.
These models are
- Whitelisting model
- Blacklisting model
- Hybrid model
Whitelisting model: Only the pre-approved traffic that meets the configured criteria is allowed by the firewall. This model is best suited for use on internal networks, which are used only by a limited group of users. The simple reason is that legitimate requests and traffic can be blocked through a whitelisting method if used on public websites and applications.
Blacklisting model: Using pre-set signatures, the firewall prevents known vulnerabilities, attack signatures, and malicious actors from accessing the online application or server. For example, if a specific IP address is sending more requests than usual, then it can protect the application against a DDoS assault by blacklisting them.
Hybrid model: Based on the application’s demands, the firewall is configured to include both the whitelisting and blacklisting methods. It operates on both private and public networks.
Intelligent Web Application Firewalls are equipped with global threat databases and machine learning capabilities, allowing them to continuously monitor web traffic and apply what they’ve learned to secure online applications.
Managed Web Application Firewall guarantees the learnings are precise and relevant. They are focused on reducing the risk associated with the applications.
Summary:
In today’s world, cyberweb attacks such as DDoS, malware, phishing are pretty common.
WAF can significantly reduce the number of threats that may compromise your online application while also providing you with peace of mind that your program is more secure.
Author,
Saketh Reddy Malepu
Attack & PenTest Team
Varutra Consulting Pvt.Ltd.




