Five Steps To Help You Prepare For Threat Hunting

Cybercriminals are very cunning and use stealthy human-led techniques with malicious intentions to carry out attacks. In the last year, around 59% of organizations have experienced complex cyberattacks. It results in cybersecurity teams opting for cyber threat hunting as an ultimate option to stop such advanced threats.
Cyber Threat Hunting
The proactive process of browsing the network for any malicious activities is known as cyber threat hunting. It is considered a more dynamic approach to cybersecurity than old and traditional methods like installing firewalls and antivirus applications. In the past couple of years, numerous organizations have encountered breaches irrespective of security measures to secure their networks from cybersecurity attacks. It means that traditional methods are no longer helpful when these threat actors use sophisticated and complex means to penetrate the network.
Threat hunting requires constantly monitoring the network for suspicious activities and vulnerabilities in the organization’s ecosystem. Furthermore, they look out for potential new threats based on analyzing the old data from various resources by developing and testing out the hypothesis based on the past knowledge collected by the cyber threat intelligence. This way, they can provide the organization with a comprehensive defense against cyberattacks. It is all due to its ability to detect, identify and mitigate any security gaps, vulnerabilities, and malicious activities present in the security infrastructure and often missed by traditional security methods.
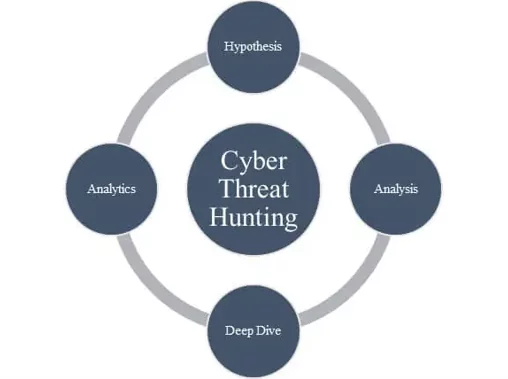
Source: HackForLab
Reasons for the Incorporation of the Threat Hunting
As per the IBM data breach security report, cyber criminals, on average, spend around 191 days inside a network without getting detected. It means they can cause severe damage in that period. Threat hunting is a systematic human-driven adaptive, iterative process that effectively minimizes the organization’s damage and risk. It also helps the organization learn its network infrastructure, systems, applications, and users in-depth. A good understanding of these components is essential for a robust security environment.
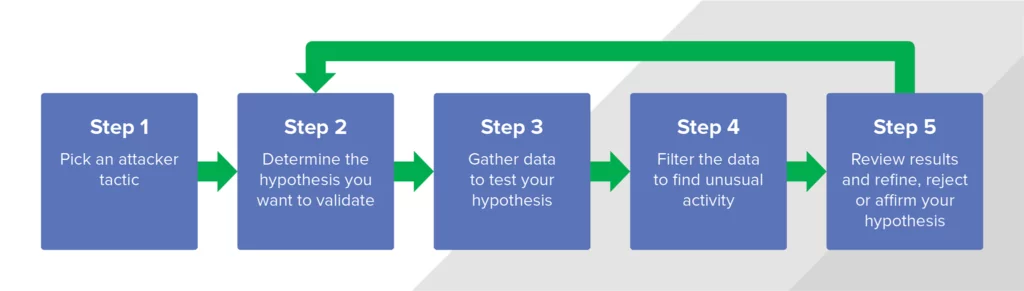
Source: ZippyOPS
Steps to Prepare for Cyber Threat Hunting
Preparing beforehand is the key to success as far as the security operations go. Therefore, laying a proper foundation before the hunt begins is mandatory. Consequently, it is recommended that an organization follow the steps mentioned below:
- Proper understanding of the maturity of the functioning cybersecurity operations: Mapping the security process to the current security model like CMMC is a great way to establish the beginning of threat hunting. It is also suggested that auditing the security posture will help determine how well the organization is susceptible to threats and risks.
- How to proceed with the threat hunting process: Once the cyber maturity has been established, the next step is to decide on how to carry out the threat hunting procedure, i.e., whether it has to be carried out in-house, outsourced, or a combination of both.
- Identifying the technology gaps: Check the existing tools and determine the requirements for efficient threat hunting and how effective is the prevention technology to be used?
- Identifying the skill gaps: Threat hunting requires the skills of the specialist. In case the organization does not have experienced in-house experts, they can go for the third-party provider and collaborate with them.
- Developing and implementing the incident response plan: An organization must have an effective incident response plan. It will help in reducing the impact of the attack on the organization.
Threat Hunting Experts
Effective threat hunting is the perfect combination of advanced next-gen technologies and human experts.
Prevention Technologies (Reducing signal disability)
Threat hunters can efficiently carry out their roles without being flooded with security alerts. It means over-usage of technologies can create confusion and hinder detection and streamlining of the investigation. Hence, delaying the response process.
Threat Hunting Technologies (EDR and XDR)
The threat hunters require investigative tools and other inputs to identify and examine for any potential threats and malicious activities. They enable the threat hunters to locate and investigate the threats thoroughly and quickly. EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) provides inputs from the endpoint solution, whereas XDR (Extended Detection and Response) combines all the signals across the IT ecosystem, including mobile, email, firewall, cloud security, and more. As a result, it helps in better detection of any potential threat.
Threat Hunting Services (MDR)
Managed Detection and Response (MDR) delivers a complete managed service. It provides customers with remote MSOC (Modern security Operations Center) functionalities. These functions help the organization detect, investigate, analyze, and respond to the threat with a proper containment and mitigation process.
Conclusion
By implementing the threat hunting program, the organization can proactively uncover many security gaps and benefit from a robust security posture. Effective threat hunting results in less work for security analysts but, at the same time, future-proofing the Security Operating Center (SOC) from known and unknown threats.
Reference
Sophos
DZone
SentinelOne
Gartner
Author,
Sanjana Yadav,
Marketing Department,
Varutra Consulting Pvt. Ltd.




