Security Advisory – Email Phishing

In today’s era, email is still used as one of the primary ways to communicate, which is not only restricted to our everyday work but also to stay in touch with our near and dear ones. Additionally, email is also used by companies to provide their services like to help a user to get online banking statements, online software updates etc. With all the benefits it provides, let us not forget the security risk it brings in. Email Phishing scams have become one of the prime attack methods used to trick a user into giving their personal information such as credit card numbers, passwords etc by performing phishing email campaign.
In mid-January 2018, security researchers reported phishing activity in which the attackers compromised MailChimp accounts to send out fake invoice notifications. At the time of discovery, security experts concluded that criminals abused weak, breached and reused credentials to hack users’ MailChimp accounts. In 2017, the same case happened with NETFLIX members. They got phishing mail asking them to restart their membership. According to a survey of Symantec 2018 Internet Security Threat Report (ISTR), by the end of 2017, the average users would have received 16 malicious emails per month.
Phishing is constantly evolving and is due to users’ unawareness and lack of knowledge about malicious URL links, attachments. This article is going to help you understand how phishing scam happens, how to identify them and protect yourself.
How attackers perform malicious activity?
The following example illustrates a phishing scam attempt
1. Attacker Creates a Phishing Page:
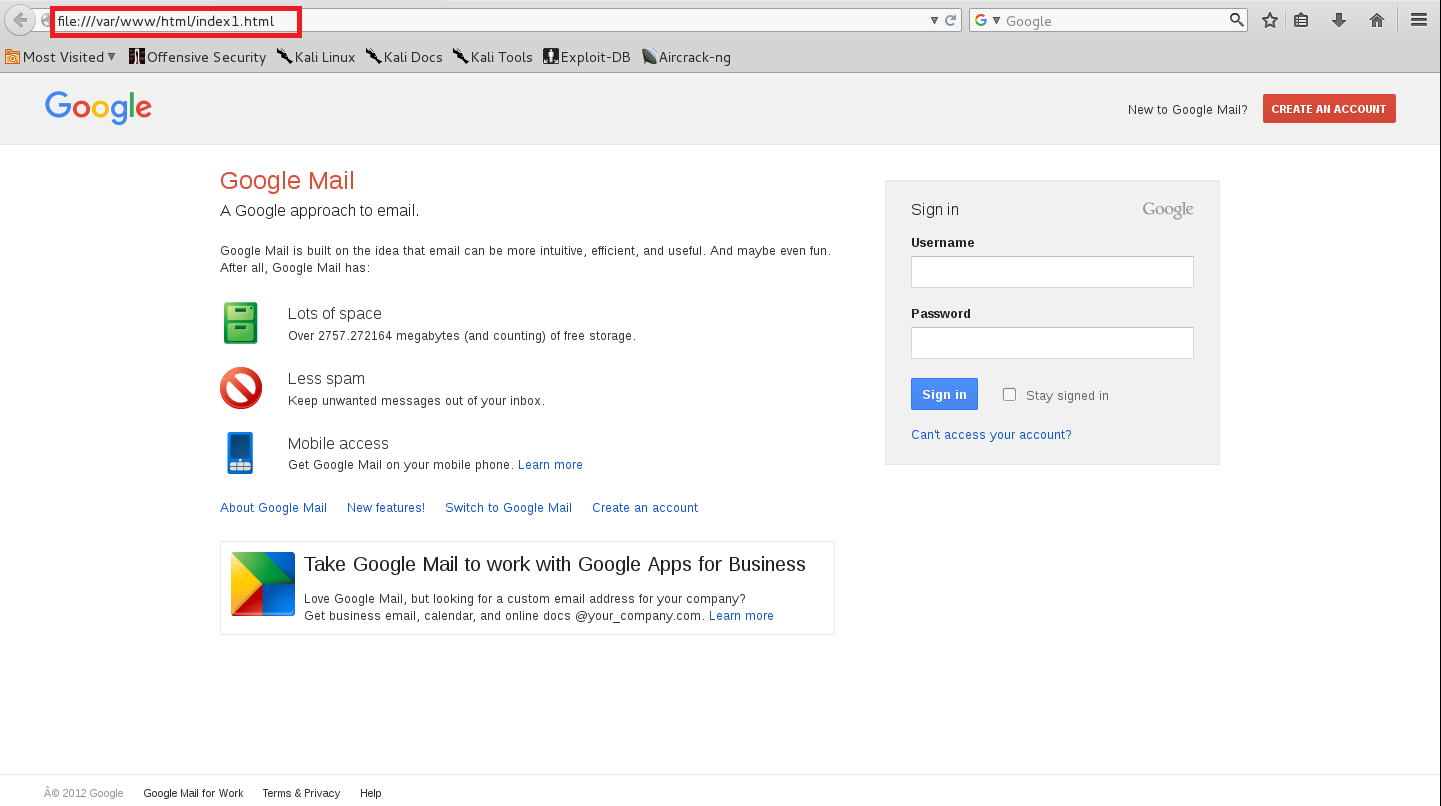
An attacker creates a phishing page (malicious page) which looks like a legitimate page using different framework techniques. An attacker then hosts that phishing URL by using free or paid web hosting server. This malicious link is attached to the fake email generator tool which sends fake mail to victim asking about their personal information.
 PoC: Phishing page
PoC: Phishing page
2. Victim Enters Credentials:
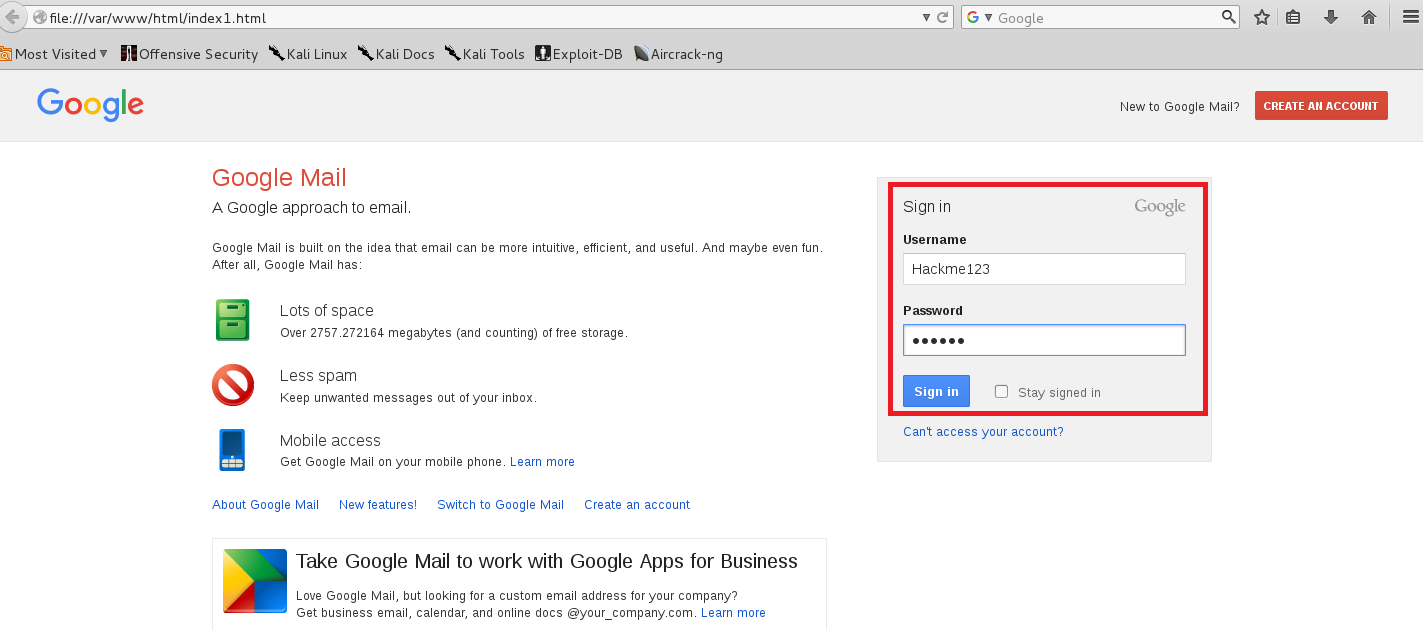
Without verifying if the link belongs to an original domain, the victim unknowingly clicks on a malicious link. This link is connected with the phishing page created by the attacker. As phishing page looks exactly like the legitimate page .He/she enters their personal sensitive information e.g. user credentials, banking information, personal information etc.
PoC: User Credentials
3. Information Captured by Attacker:
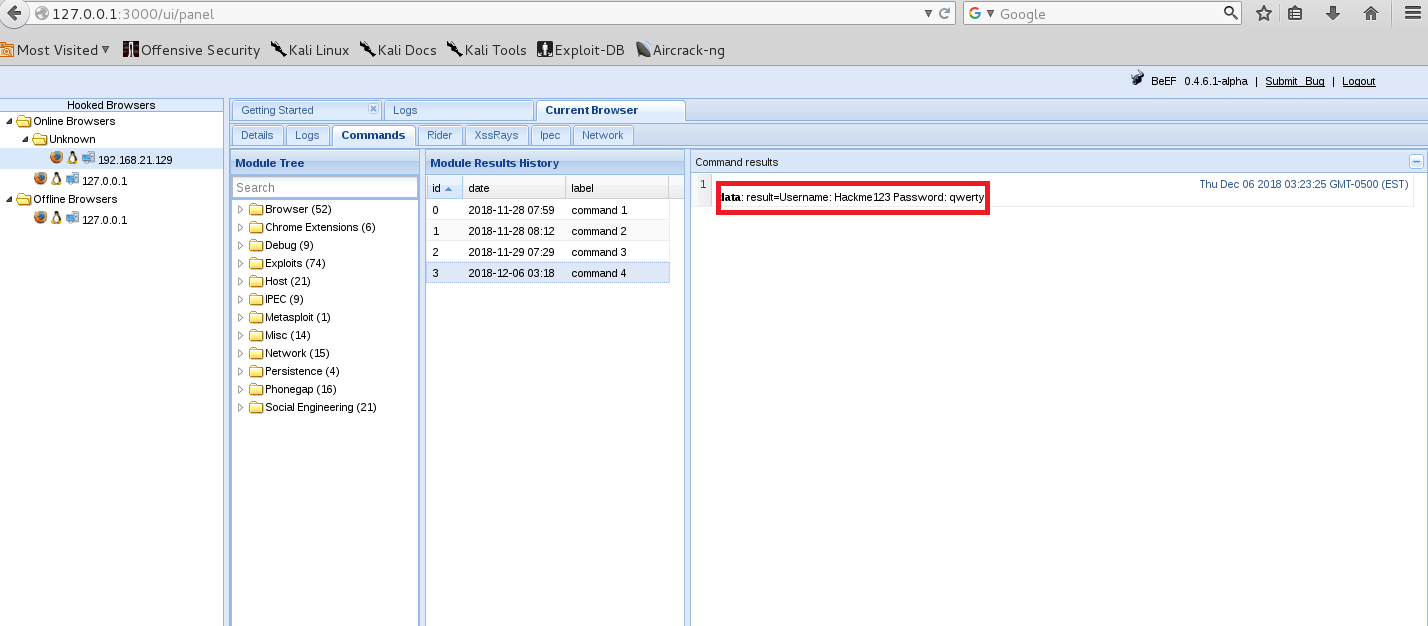
As phishing page is linked with the attacker database server, any data fed by the victim to the malicious page is accessible by the attacker. By using this information, an attacker can carry out further malicious activities.
PoC: Credentials captured by the attacker
How to identify a phishing email?
1. Always be suspicious:
Phishing emails try to freak you out with warnings of stolen information and then offer an easy fix if you just “click here”. When you are in doubt open your browser, go to the company’s website, then sign in normally to see if there are any signs of strange activity. If you’re concerned, change your password.
2. Detect a fake link:
To find a fake mail, you can move your mouse on the link. You will see the real link pop up after a few seconds. You could right-click on the link, copy it and then paste it into a text document to see where it would really redirect you to the original website. When you are looking at the URL look for any spelling mistakes in domain name. A fraudulent email might link to http://www.ex@nullmple.com instead of http://www.example.com
3. Check the instruction:
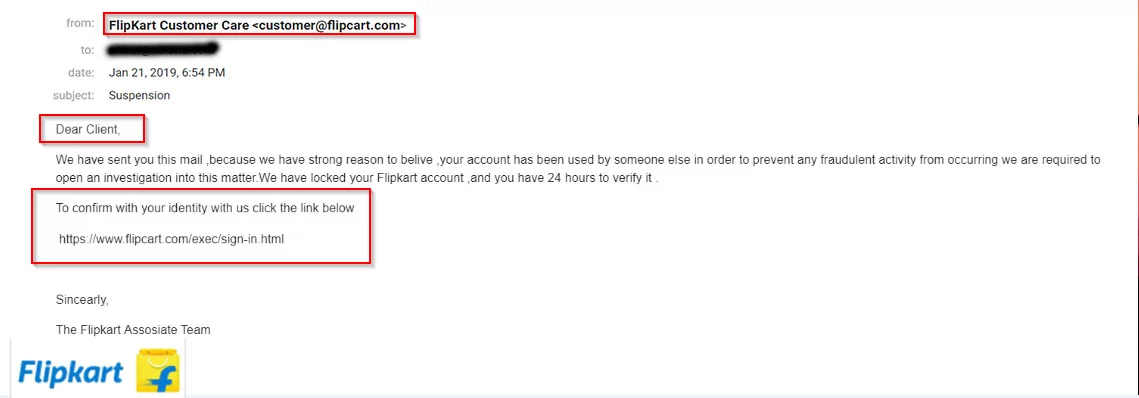
Any legitimate company that’s sending a security notification will never ask you to click a button or link or download an attachment. The attacker will tell you to go to its website home page and log in to your account from there. Also, an attacker might tell you to call customer service with any questions.
PoC: How to identify phishing email
How to avoid email phishing scams?
1. Implement strong authentication:
Use two-way verification method. Even though your account credentials were stolen attacker will not be used that account for doing any criminal activity.
2. Do not click on attachments:
You should not click on the attachments sent by any anonymous email id. It might contain malware that can damage files on a victim’s computer, steal passwords or spy online activity without their knowledge.
3. Deploy a SPAM filter:
Downloading a good spam filter is essential to catch phishing emails before they end up in an inbox and to prevent accidental opening of malicious attachments through an unwary user.
4. Deploy a web filter to block malicious web applications:
A browser-integrated anti-phishing solution, such as SpoofGuard and PwdHash, could provide effective help by protecting against unauthorized IP and MAC addresses to prevent and mitigate online scams.
5. Conduct training sessions with mock phishing scenarios:
In most cases, phishing attack requires user action to succeed so it is obvious to make the employee aware.
Conclusion
Phishing is a form of social engineering attack used to collect personal, banking information etc. from the affected victim. It is important to stay aware of the different phishing techniques and to keep your computer and internet browsers up to date with current antivirus and security patches. Be Safe!
Author,
Aniket Shinde
Attack & PenTest Team
Varutra Consulting