Zooming Security Vulnerabilities [Part – 1]

Diving into Zoom Security Vulnerabilities [Part – 1]
Introduction –
Zoom is a popular web-based video-conferencing application available to be installed on computer systems and mobile devices that enables users to use online video conferencing services.
Zoom application offers top-quality video, audio, and screen-sharing options with high performance and is available across various platforms.
Recently attackers are attempting to use numerous methodologies through which they are able to exploit the vulnerabilities residing within the application. This blog article talks about a few of the critical vulnerabilities which are making use of the Coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic as mentioned below:
1. Zoom Lookalike Domains –
As Zoom is widely used as the video conferencing solution because of the ongoing Corona pandemic and due to the travel restrictions for various business groups and in work from home scenarios, attackers are taking its advantage and have registered numerous Zoom themed domains for malicious purposes.
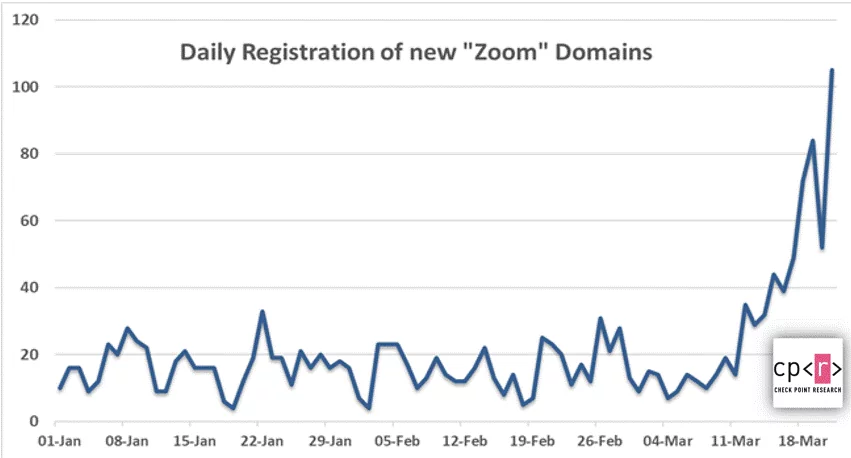
Image Source – Check Point Technologies Blog
Researchers have discovered malicious files using a zoom-us-zoom_##########.exe an “microsoft-teams_V#mu#D_##########.exe” (# representing numerous digits). Once the file is executed, it will try and install unwanted third-party applications and malicious payloads.
Image Source – Check Point Technologies Blog
2. Malicious Zoom Installer –
Malicious Coin digger is clubbed with the legitimate installer of Zoom video conferencing application, luring users who want to install the software but end up unwittingly downloading a malicious file, note that these compromised files are not from Zoom’s official website.
Users who try and download the installer (from lookalike domains and malicious domains) download the AutoIt compiled malware which is termed as – Trojan.Win32.MOOZ.THCCABO
It also checks whether the Microsoft Smart Screen and Windows Defender are enabled and any antivirus solutions running within the system to evade malware detection.
Image Source- Bleeping Computer
3. UNC Path Injection Vulnerability –
It was discovered that Zoom client for Windows is at risk against UNC path injection vulnerability which could allow remote attackers to steal login credentials for victim’s Windows systems. After stealing the information, the victim’s system is exploited to launch any program already present on a victim’s computer or execute arbitrary commands to compromise it remotely.
The attack involves the SMBRelay technique where Windows automatically exposes a user’s login username and NTLM password hashes to a remote SMB server when attempting to connect and download a file hosted on the SMB server.
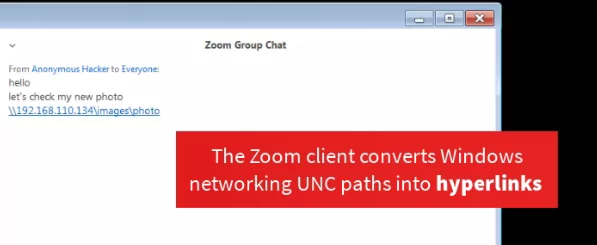
Image Source: Medium.com
Recommendations for UNC Path Injection Vulnerability –
Windows users can change the security policy settings to restrict the operating system from automatically passing their NTLM credentials to a remote server.
This policy is called ‘Network security: Restrict NTLM: Outgoing NTLM traffic to remote servers and is found under the following path in the Group Policy Editor.
Path – Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Local Policies -> Security Options -> Network security: Restrict NTLM: Outgoing NTLM traffic to remote servers.
4. GHOST Vulnerability –
Zoom application is additionally at risk of GHOST vulnerability which is a buffer overflow bug that affects function calls in the Linux Glibc library.
This vulnerability poses a risk of remote code execution attacks. An attacker who exploits this flaw can gain complete control of the compromised system.
5. Zoom-Bombing –
“Zoom-Bombing,” an uninvited intrusion on video calls that affects various virtual classes and business calls.
To Zoom-bomb, attackers find ways to enter Zoom calls they weren’t invited to, either by receiving the password from others within the call, typing out a random code in the hopes that it is a real meeting ID, or finding a link in a social media post or elsewhere on the internet.
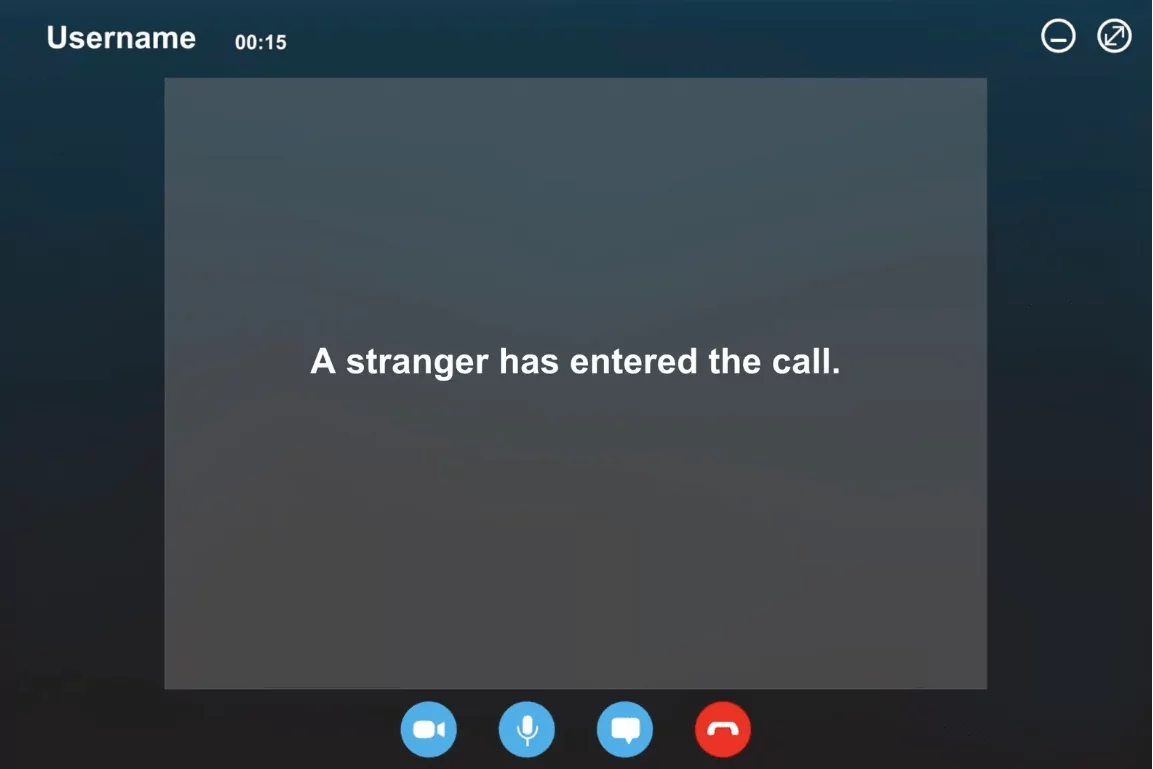
Image Source: Shutterstock/Illustration by Rachel E. Greenspan
6. Hackers Exploiting Zoom Vulnerabilities to Record Meetings –
It was discovered that a vulnerability in the Zoom application exists that injects malware into the Zoom process and then records Zoom meeting sessions, also captures the chat text without any user interaction even when the recording option is disabled by the meeting organizer.
At the time of recording, it is believed that none of the participants are aware that the session is being recorded,
Shockingly, the attack is possible with the latest version of Zoom with all the security features turned on and antivirus software installed and running.

Image Source: gbhackers.com
Distribution Methods –
Phishing Emails, Phishing Domains, Malicious Websites, Unpatched Zoom Application
Recommendations –
- Avoid using Zoom if possible, and check for an alternative video-conferencing application.
- Beware of lookalike domains, spelling errors in emails and websites, and unfamiliar email senders.
- Be cautious with emails and files received from unknown senders, especially if they are offering special deals or discounts.
- Users are advised to download installers from the application’s official websites to avoid any system compromise.
- Keep a reliable and tested backup of data that can be restored in case of business emergencies.
- Educate users that they should not open attachments from unknown emails.
- Block the IoC’s as listed in the blog article on applicable security solutions.
- Do not open attachments in unsolicited emails, even if they come from people in the contact list, and never click on a URL contained in an unsolicited email, even if the link seems benign.
- Exercise caution while visiting unknown links or web pages.
- Avoid sharing links via social media and try to ensure only trusted colleagues or participants join the meeting.
- Avoid using Zoom Personal Meeting ID (PMI) to host events and meetings and use a custom meeting passwords every time.
- Keep AV signatures as well as the operating system and 3rd party application patches up-to-date.
References –
- https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/hackers-take-advantage-of-zooms-popularity-to-push-malware/
- https://blog.checkpoint.com/2020/03/30/covid-19-impact-cyber-criminals-target-zoom-domains/
- https://blog.trendmicro.com/trendlabs-security-intelligence/zoomed-in-a-look-into-a-coinminer-bundled-with-zoom-installer/
- https://thehackernews.com/2020/04/zoom-windows-password.html
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) –
URLs:
2no[.]co/1IRnc
hxxps://2no[.]co/1O5aW
Hash Values (SHA 256):
d65e8a784c2ba0d9f7a029e1817b78b31324fb8c988e0467fd693b0efd890756 (Installer)
04b560d234e8706d5e43532e9e674ee54ed6f63d62795fb0e5776e23da7eb4d8 (64.exe payload)
Note – It is highly recommended to read the zooming Security Vulnerabilities Part – 2 articles.
Blog Authors –
Poornima J. / Ashish M.
Security Consultants – Varutra Managed SOC




