Exploit Kits: Attackers Preferred Exploitation Tools

Exploit Kits: Overview
Cybercrime was once the domain of a tiny handful of people with excellent technical skills who leveraged their abilities for malicious acts. However, cybercrime had grown now into a multibillion-dollar business, with threat actors profiting from the sale of malware, ransomware, and exploit kits on Dark Web forums – which is the hidden internet.
According to a survey conducted by cyber threat intelligence firm CheckPoint Research, education and research are the sectors most affected by cyberattacks in 2021, with an average of 1,605 attacks per institution per week, representing a 75% increase from 2020.
Other sectors, such as the government/military, have experienced 1,136 attacks per week in 2021, an increase of 47% from 2020. Also, the communication industry has seen 1,079 cyberattacks per week, jumping 51% over 2020. In addition, Africa experienced the most significant number of attacks in 2021, with an average of 1,582 weekly attacks, an increase of 13% from 2020.
Exploit kits are a well-known technique for cybercriminals to attack victims’ devices since they enable covert ways to breach systems via automated software. It can be sold for thousands of dollars on underground hacker forums.
Cybercriminals initially target users through initial infection vectors such as malvertising and spam emails. When users click on the malicious link, they are routed to hijacked websites or custom-built pages. Next, they are embedded with exploit kits that exploit known flaws that drop harmful software such as trojans, ransomware, and other malware on victims’ PCs successful exploitation.
Exploit kits were developed to enable threat actors to automate a sequence of procedures that lead to the delivery of malware payloads to vulnerable devices while accessing the web.
Exploit-Kit-as-a-Service: EKaaS
Exploit-kit-as-a-Service is a SaaS (Software as a Service) business model that allows people with less technical knowledge to buy and rent pre-developed exploit kits. This kit can compromise vulnerable systems, increase the attackers’ income, and increase the malware infection rate.
The following factors have made it freely available in underground hacker forums to all users.
- No Expertise Required– Users who have no technical expertise can also use exploit kits as it is equipped with pre-coded and user interfaces. It allows attackers to customize them as per their requirements.
- Low on Cost– Exploit kits can be found reasonably priced on many hacker forums on the Dark Web.
- The versatility of Malware– From banking trojans to ransomware, exploit kits may distribute various malicious software.
- Abundantly Vulnerabilities Targeted– Multiple flaws discovered in key software such as Google Chrome, Microsoft Internet Explorer, Adobe Reader, and more increase the attacker’s interest in obtaining an exploit kit that can efficiently exploit the flaws.
- Evade Detection– Sophisticated exploit kits employ various techniques to avoid detection by anti-virus software, which might result in many infections and boost the attackers’ revenue.
- Offer Technical Support– Some exploit kits even offer technical support to help clients who cannot operate features on their own or try to access sophisticated features.
- Use Bitcoins for Payments– Most exploit kits employ cryptocurrencies as a payment mechanism to avoid being detected and caught by law enforcement personnel.
Exploit Kits: Workflow
- In the first step, attackers deceive users into accessing genuine sites that have been infected with a sophisticated exploit kit.
- The victims are redirected to the exploit kit landing page in the second step.
- In the third step, the malicious landing page analyses the victim’s system for vulnerabilities.
- In the fourth step, the malicious kit leverages the reported flaw and attempts to install malicious software on the victim’s PC, such as a banking trojan, ransomware, or crypto miner.
- Lastly, the deployed software executes ransomware payloads, encrypts system data, and demands millions of dollars for the decryptor in the fifth step.
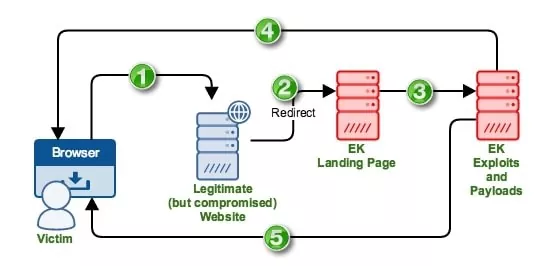
Image:
Workflow of Exploit Kits
Well-known Exploit Kits and Vulnerabilities Exploited
- Angler Exploit Kit
Angler exploit kits were initially identified in 2013 and have quickly become one of the most prominent exploit kits used in cyberattacks due to their unique methods in spreading ransomware variants, including UmbreCrypt, Kovter, TorrentLocker, CryptoWall, and TeslaCrypt.
Furthermore, the Angler exploit kit used to be one of the few exploit kits that allowed fileless infections. As a result, the malware was never executed on the HDD and lived in memory to avoid detection.
- Fallout Exploit Kit
Fallout EK was launched on September 7, 2018, by “FalloutEK,” a member of the Russian-language underground hacker community, and was initially advertised on hacker sites for $50 per day, $250 per week, or $900 per month, before being raised to $400 per week or $1,300 per month. FalloutEK is also known to collaborate with other ransomware partners who promote the sale of exploit kits, such as GandGrab, Maze Locker, Kraken Cryptor, Matrix, and Minotaur.
Fallout EK restricts its clients to 25 and hosts the instance on a different server for each client as an extra layer of security to monitor organizations’ activity using unique, personalized shellcode. Egypt, Japan, South Korea, Pakistan, India, Philippines, Morocco, Algeria, Indonesia, Turkey, and Iraq were the primary targets of this exploit kit.
- RIG Exploit Kit
On June 18, 2014, “TakeThat,” a Russian-speaking member of hacker forums such as Verified, Club2CRD, and Exploit, posted a sales thread for the RIG Exploit Kit (RIGEK). He rented it on dark web forums for $50 per day, $200 per week, or $700 per month, which distributed several ransomware variants such as CryptoShield, BartCrypt, Princess Locker, YafunnLocker, and more. In addition, this RIG Exploit Kit was used to spread different malware in campaigns such as Pitty Tiger, FormBook, Afraidgate, DragonFly, Deep Panda, and ProMediads, and the RIG Exploit Kit exploited several vulnerabilities.
- Neutrino Exploit Kit
The Neutrino Exploit Kit, used in CryptoWall and CryptXXX ransomware operations and ShadowGate, Afraidgate, and ProMediads campaigns, was observed in 2012 was available for hire at $40 per day or $450 per month. Furthermore, in 2015, this exploit kit was used in landing pages that exploited Flash Player vulnerabilities to install CryptoWall 3.0 ransomware on victims’ systems which affected the computers by exploiting several system software vulnerabilities.
- Phoenix Exploit Kit
The Phoenix Exploit Kit, first discovered in 2007, was responsible for most Web-based attack activity in 2010. It was closely associated with ransomware groups such as AnteFrigus, CryptFIle2, CryptoShield, BartCrypt, YafunnLocker, Spora, and FessLeak in Pitty Tiger, FormBook, Afraidgate, DragonFly, Deep Panda, and ProMediads.
Security Best Practices to Counter Exploit Kits
- IT System administrators should ensure that all corporate systems, devices, and software are running with the latest security updates.
- IT Security administrators should Identify and prioritize the patching of vulnerabilities that have a “critical” or “high” risk score and are actively exploited by threat actors.
- Remote Desktop Services should be restricted only to authorized personnel and accessible only via VPN, rather than accessible over the internet.
- IT System administrators should regularly take Backup of the databases, applications, and all critical data owned by the organization.
- Users should use intense and complex to guess passwords never re-use the same password at multiple sites.
- Users should not open any unknown attachments or click on anonymous advertisements/links displayed on untrusted websites.
- Users should enable the “Safe browsing” option under “Privacy and security” settings in web browsers to block harmful websites from being accessed.
- Users should use Anti-virus and Anti-spyware software to monitor, detect and mitigate malware threats from their systems.
Conclusion
Exploit kits are more complex tools that contain many exploits and are designed to automatically exploit vulnerabilities on victims’ PCs while they surf the web. Since they are highly automated and adaptive, they have become one of hackers’ preferred strategies for large-scale malware and ransomware distribution. Because of its adaptability, ease of use, and low cost, any inexperienced user may employ it to conduct malicious operations.
References
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/security/threat-protection/intelligence/exploits-malware
- https://www.recordedfuture.com/exploit-kits-delivering-malware/
- https://heimdalsecurity.com/blog/exploit-kits-service-automation-changing-face-cyber-crime/
- https://www.tripwire.com/state-of-security/security-data-protection/cyber-security/4-factors-behind-the-rise-of-exploit-kits-as-a-service/
Author,
Abhishek Hiremath,
Associate – Managed SOC [ L1 ],
SOCGTM Department,




