Ransomware Trends: Higher Ransom Demands, More Extortion Tactics
Ransomware attacks have been a severe issue for the past couple of years and are evolving daily. Organizations widely incorporate advanced cybersecurity technologies and improvised response processes for ransomware. They are comparatively more successful than battling traditional ransomware attacks. The traditional ransomware attacks have been successfully subdued. But with time, these attacks have also evolved and are known as modern ransomware attacks. Among various cybersecurity threats, ransomware trends are higher than other attacks. Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 has published a ransomware threat report. According to which incident responders and researchers provide an in-depth analysis of the ransomware threat groups demanding ransom by threatening the victim to release their sensitive and private information.
In 2021, there was a 144% increase in the average ransom demand in 2020. There has also been an 85% rise in the victims whose personal information was posted on the dark web. It shows how cyber threat actors have profited from extortion and transformed themselves into big enterprises. This cyber extortion has reached a crisis level due to its success and developed into a business module called RaaS (Ransomware as a Service).
The Appearance of the Modern Ransomware Attack
Modern ransomware threat actors track victims with valuable, sensitive data. Then, they exfiltrate it rather than encrypting it from the victim’s network. By doing so, they demand ransom from the victim and threaten to expose their data. Organizations have a great deal of customer data, and sensitive information, if leaked, can lead to severe issues like lawsuits, regulatory penalties, and damage to reputation. The treat actors take significant time to monitor the victim and take over different parts of the victim’s network before executing the ransomware payload. It completely takes over their network through various human-monitoring stages by deviating them from click-on-the-link inevitable activities. These treat actors ensure the attacks look like an advanced persistent threat (APT) rather than a traditional ransomware attack.
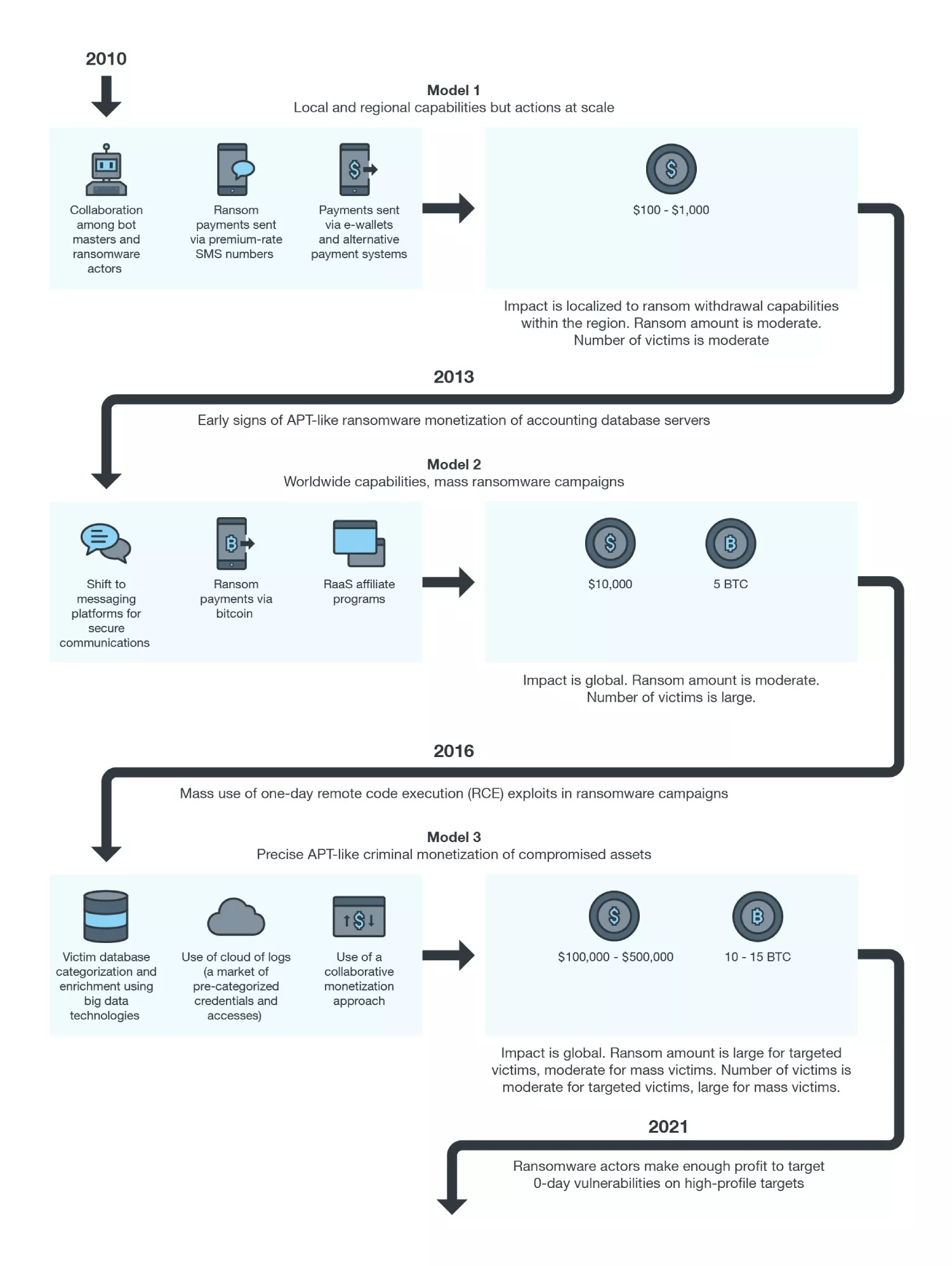
Source: Trend Micro
Reason for Frequent Ransomware Attacks
There has been a rise in ransomware attacks, which are also getting evolved daily. Several reasons are contributing to this factor:
- The availability of malware kits in the market enables the threat actors to create a new malware sample on demand.
- The knowledge of exceptional generic interpreters can help develop cross-platform ransomware like Ransom32 that uses Node.js and a JavaScript payload.
- The new technologies enable complete disk encryption rather than selective files.
Cybercriminals can create malware with the assistance of advanced technology and don’t even need to be tech-savvy. The ransomware marketplace is gaining popularity as it provides malware strains to any cyber crook who can generate profits for the malware creators.
Trending Ransomware Groups and Payment Demands by Them
According to the Unit 42 security consultants, the average ransom demand for cases grew 144% in 2021 to $2.2 million, while the average payment rose to 78%, approximately $542,010. WannaCry, Petya, CryptoLocker, and TeslaCrypt are some famous ransomware examples.
It is said that a ransomware threat group known as the Conti ransomware group is mainly responsible for most of the attacks. It is followed by REvil (also known as Sodinokibi), which is in the second position at 7.1%. Finally, Hello Kitty and Phobos are at 4.8% each and hold the third position.
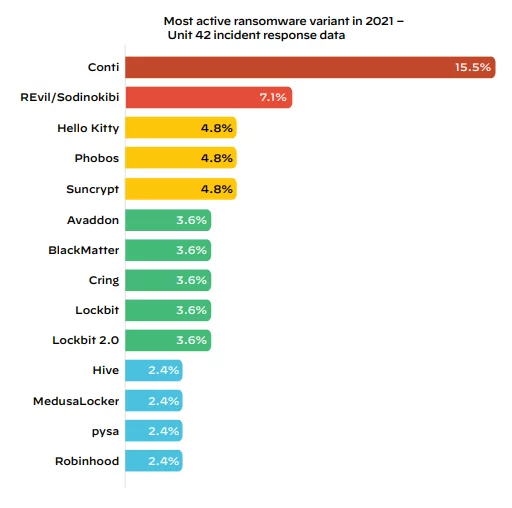
Source: Palo Alto Networks (2022 Unit 42 Ransomware Threat Report)
It is said that after the data loss, it may take weeks and months to recover from the incident thoroughly, and the idea of paying the ransom to retrieve the data looks tempting. But there are various reasons why paying the ransom to the threat actors is terrible.
- There are chances that the threat actors may take the payment and not provide the decryption key. It depends on their integrity.
- The cybercriminals may make repeated ransom demands as you have already paid and know you are at their mercy. This way, criminals can paint a target on your back, knowing they can extort money and make a good profit. There may be a chance they can repeatedly attack after some time to extort money again or announce to other criminals that you are an easy target and making money from you is easy.
- The threat actors can provide a faulty decryption key. Sometimes encryption process also damages the files, and they are beyond repair. In such a scenario, a decryption key may be unable to unlock the files and may be lost forever.
- You are indirectly funding a criminal activity or promoting them. By paying the ransom to the cybercriminals, you are indirectly encouraging their behavior to continue doing so. There is no guarantee that after spending the document, your data is safe, and you can exceed it. They may fool you or target you after some time as they know you can pay the ransom.
Data Published on the Leak Sites of Dark Web and the DDoS-Double and Multi-Extortion
For the past couple of years, some high-profile cyberattacks have hindered the daily life of people and obstructed people from carrying out simple everyday tasks. Moreover, these ransomware threat actors have evolved and using additional means to extort money from their victims. For instance, threat actors gain access to the victim’s data and prevent the victim from accessing it by decrypting it and demanding a ransom to provide the key in most cases. But some cybercriminals use the double extortion method by using the dark web leak sites to threaten the victim into releasing their sensitive data to the public. In addition, some groups harass the victims, bring the websites down or cause harm to others by gaining access to sensitive information.
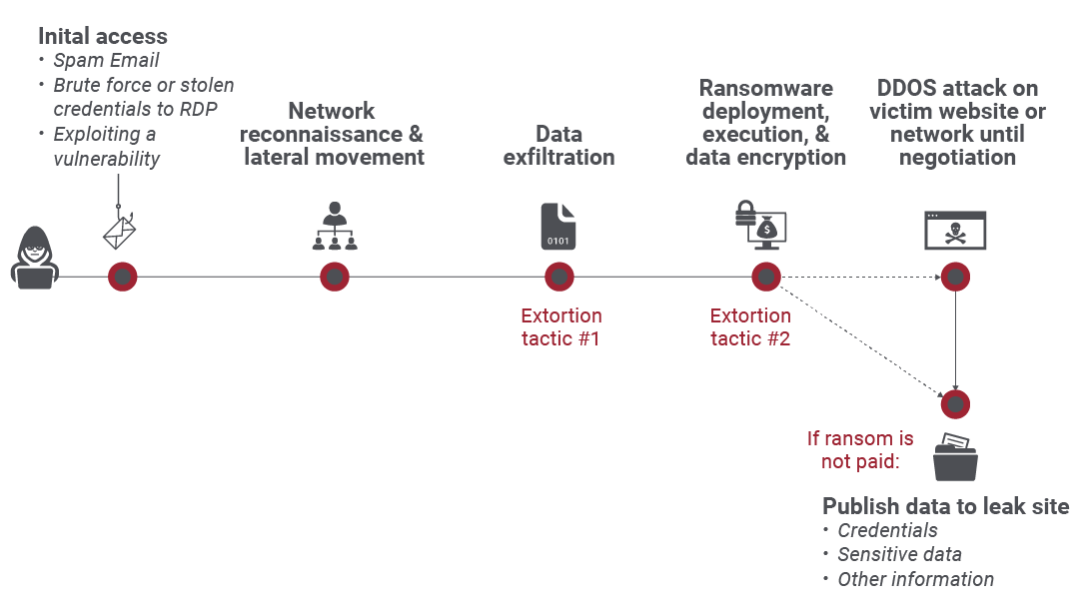
Source: Zscaler
This ransomware trend is known as multi-extortion, which rose in 2021. As per a survey, 60% of the dark web leak site data were in America, followed by 31% from Europe, Africa, and the Middle East, and then 9% from the Asia Pacific region. The most affected industries are wholesale, retail, healthcare, construction, legal services, and manufacturing.
Conclusion
Ransomware attacks are increasing day by day. These threat actors are just waiting for a single opportunity to access your system through malware attacks, phishing, and more. So, it is always advised not to open or click on an unfamiliar email or links, along with maintaining cyber hygiene. Organizations can also prepare themselves by consulting cybersecurity companies for assistance.
Reference
Palo Alto Networks’
Trend Micro
Trellix
Author,
Sanjana Yadav
Marketing Department,
Varutra Consulting Pvt. Ltd.




