Top 10 Cybersecurity Threats

There is a significant shift in the digital landscape as people rely on the internet more and more across the globe. But unfortunately, it also means we are open to cybersecurity threats and attacks from hackers with malicious intentions. According to the annual cybersecurity report from Cisco, there has been a substantial increase in cyber-attacks. The hackers can launch campaigns through a wide range of network-based ransomware without any human inference.
Top 10 Cybersecurity Threats
Read about the top 10 cybersecurity threats that you need to look out for:
Phishing Attacks
Phishing in cybersecurity is considered to be one of the common cyber-attacks. The hackers generally send out malicious emails to unsuspecting users pretending to be an authentic and reliable sources. Then, the hackers add a malicious link or an attachment that permits them to access the victim’s system, install malicious files, or extract personal information. These attacks can also occur through social networks, online communities, or direct messages. The hackers use the social knowledge available on the victim’s public forum to interact with them and then steal their sensitive information. According to Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report in 2021, it was observed by the researchers that phishing attacks were the cause of 36% of data breaches which is 22% more than the previous year.
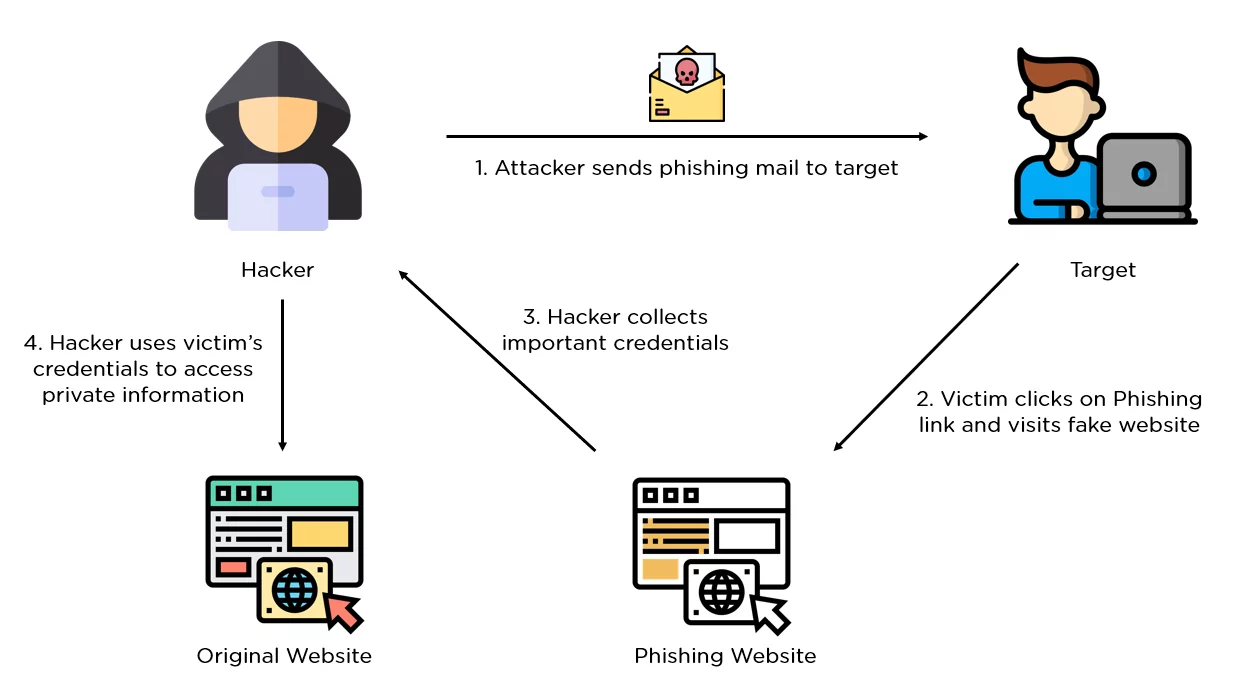
Source: Simplilearn
Here are different types of phishing attacks:
- Spear Phishing: This phishing attack directly targets a specific organization or an individual.
- Whaling: It is an attack directed within the organization, especially toward the stakeholders and senior executives.
- Pharming: Through this attack, the hacker captures the user credentials by creating a fake login page by leveraging DNS cache poisoning.
Phishing attacks can also occur through a fake phone call or text message. It is known as voice phishing and SMS phishing, respectively.
IoT (Internet of Things) Attacks
The Internet has made our lives easy. Devices are now interconnected through the internet for convenience and ease. Unfortunately, it also means an opportunity for cyber-criminals to exploit the devices and wreak havoc. The connectivity causes the hacker to breach or penetrate through an entry point and use it to control other devices as well that are connected to the same network. IoT attacks in cybersecurity seem to become widespread due to the demand for IoT devices. The Fortune Business report states that the IoT market will grow to 1.1 trillion by 2026, which means the opportunity for attacks will also increase. Generally, IoT devices are not very secure in terms of security. Some of the practices that will help in tightening the security of your IoT devices are:
- Updating the OS regularly.
- Using strong passwords for IoT devices.
- Changing the passwords regularly.
Malware
The term malware is a common term that includes various cyber-attacks like viruses, worms, and spyware. It exploits the vulnerability by breaching the network to install a malicious application or software into the device or system as the user clicks on the unsafe link or attachments. After gaining access to the system, the hackers can easily access sensitive and private information, damage the system or render it unworkable and deny access to critical applications and components.
Here are some malware types that you need to be aware of:
- Ransomware: It is a typical malware that gains access to the user’s system, denies them access, and threatens them to publish their sensitive data until they pay a ransom. There has been an occasion when advanced ransomware is used for crypto-viral extortion. The hackers encrypt the user’s data and demand ransom to decrypt the data. In Check Point’s mid-year report security report, ransomware attacks have increased over the past year, with 93% more carried out in the first and second quarters of 2021. According to the US Treasury Department report, it is estimated that $590 million in suspicious activity is linked to ransomware attacks in the first half of the year. While for overall 2020, the amount was just $410 million.
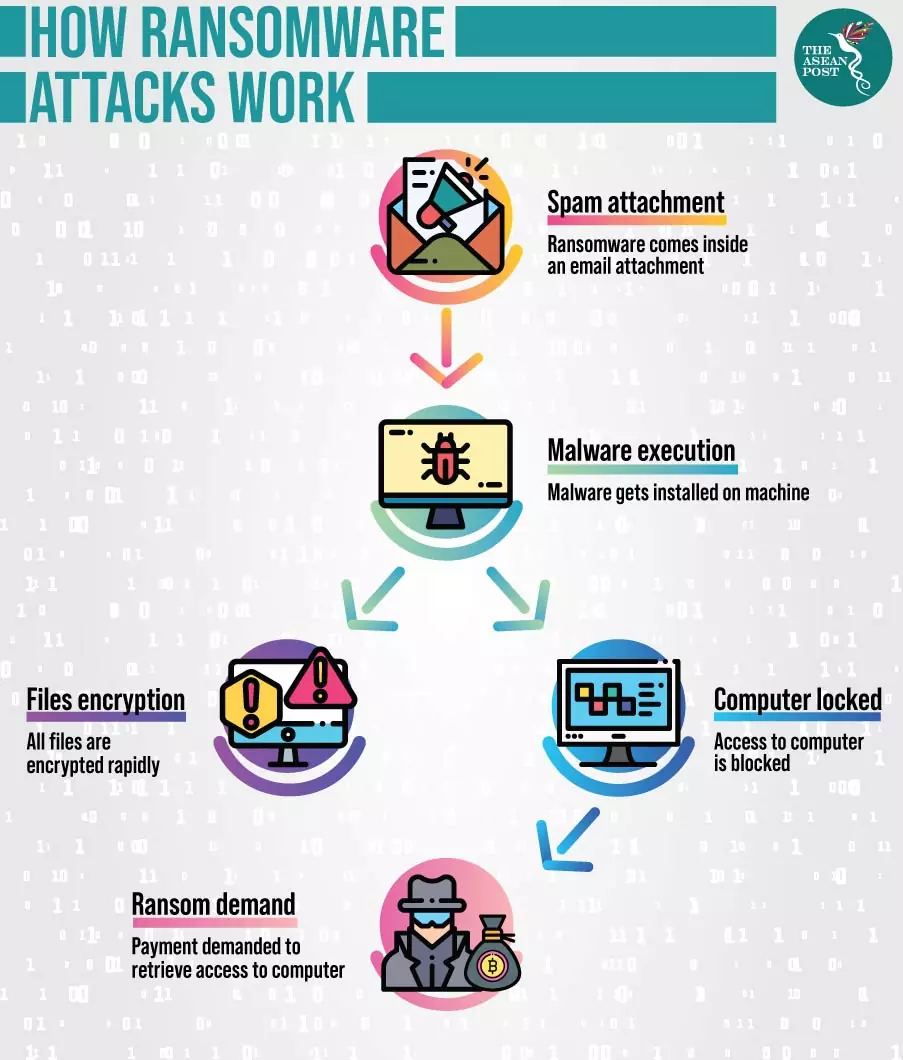
Source: The Asian Post
- Spyware: As it suggests, this malware is used to spy on users and collect their private information. The cyber-criminal can later use this information to blackmail them or install malicious applications on the system.
- Viruses: Viruses corrupts the software and latches themselves to the initialization sequence. They replicate themselves and corrupt other codes in the system. They attached themselves to executable code and repeated themselves by creating a new file that contains a virus with the same file name but a .exe extension.
- Trojan: Trojans are slightly different from viruses as they cannot replicate themselves but are generally used to create a backdoor for the hacker to be exploited later on. It is an application that is hidden inside an application or program.
- Worms: Worms don’t attack the host but being self-contained applications, it spreads across the network. It is installed in the system through email attachments and sends a copy of itself to every contact in the email list. It is used chiefly to overload the server and carry out the denial-of-service attack.
SQL Injections
The hacker performs this attack as they insert malicious code into the server by using the SQL (server query language) and compelling the server to deliver protected data. It involves submitting infected code into the unprotected website search box or comment box. It permits the backend to run malicious queries when the parameter is used in the SQL command rather than inserting values directly. Also, the SQL interpreter uses the parameter as a form of information rather than executing it like a code.
Denial-of-Service (DOS) Attack
DoS attack in cybersecurity is to overflow the system, servers, or networks with overload resources and bandwidth. It results in the system getting overloaded and unable to carry out any operations. It can also be referred to as Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks. Their primary goal is to saturate the system’s resources by delaying response to service requests. They also try to take the approach offline, creating a way to enter into a network or server. Some of the most common DoS and DDoS attacks are teardrop attacks, botnets, TCP SYN flood attacks, smurf attacks, and ping-of-death attacks.
Zero-Day Exploit
The Zero-Day exploit in cybersecurity is an attack that exploits the network vulnerability before the security patch for the software, or an application is released or implemented. There is a small window before the application is vulnerable before the patch is released, and the attacker uses that window to exploit the application. So, constant monitoring, making proactive decisions, and following threat management practices are required to prevent this exploit from occurring.
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT)
As the name suggests, the APT in cybersecurity is an attack that uses sophisticated hacking techniques to get the system access. They then remain undetected in the system or server for a long time, resulting in damaging consequences. It is a highly complicated and sophisticated attack and needs a lot of effort to carry out, and it only targets high-value people like large organizations or more. But it does not mean small and medium industries cannot be targeted. Some hackers have attacked small enterprises in the supply chain and made their way to large organizations. They use such companies as a stepping stone as they are not as secure as the large organization.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
As the name suggests, the Man-in-the-Middle attacks in cybersecurity are attacks where the attacker intercepts a transaction happening between the people and insert themselves in the middle. The attacker can manipulate and steal the data by interfering with the traffic in simple terms.
This type of attack generally exploits the network’s vulnerabilities like public Wi-Fi and injects itself between the web (internet) and the victim’s device. It is tough to detect and often thinks the information they provide is being used by a legitimate and authentic party or destination. Malware or phishing attacks are always used to carry out MitM attacks.
Cryptojacking
Cryptojacking is a type of cyber-crime that uses unauthorized users’ devices to mine cryptocurrency. Like other cyber-attacks, its motive is not about data stealing but about making profits and remaining hidden. Cryptocurrency mining requires a lot of computer processing power, so hackers make money by secretly cloaking themselves on someone else’s devices. The cryptojacked devices in any organization can cause performance issues and costly downtime. The only solution is for any IT security experts to track down and remove cryptojacking code installed in the system.
Social Engineering
Social engineering attacks gain access to personal information by exploiting the victim’s social interactions or network. Hackers manipulate to trick the victim into making security mistakes or deliver the information by pretending to know them. It is considered a dangerous cyber-attack as hackers do not exploit any system vulnerabilities, but it depends on manipulating the victim and relies on human errors.
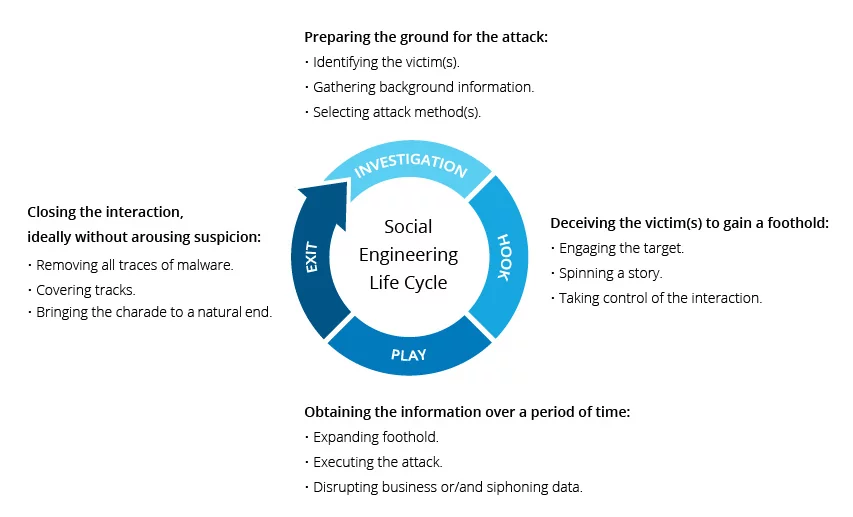
Source: Imperva
Conclusion
The cyber-attacks are getting more complex day by day. Therefore, it is suggested to include proper security hygiene and following cybersecurity preventive measures to mitigate these attacks. It is essential for an organization to keep their software and application updated, manage their threat management tools and firewalls, install antivirus software and control user privileges. This way, they can prepare themselves and prevent cyberattacks.
Reference
Kaspersky
Datto
Cybermagazine
Imperva
Author,
Sanjana Yadav,
Marketing Department,
Varutra Consulting Pvt. Ltd.



